Non-Mulberry and Mulberry Silk Protein Sericins as Potential Media Supplement for Animal Cell Culture
- PMID: 27517047
- PMCID: PMC4969515
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7461041
Non-Mulberry and Mulberry Silk Protein Sericins as Potential Media Supplement for Animal Cell Culture
Abstract
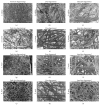
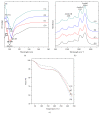
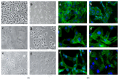
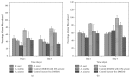
Silk protein sericins, in the recent years, find application in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals and as biomaterials. We investigate the potential of sericin, extracted from both mulberry Bombyx mori and different non-mulberry sources, namely, tropical tasar, Antheraea mylitta; muga, Antheraea assama; and eri, Samia ricini, as growth supplement in serum-free culture medium. Sericin supplemented media containing different concentrations of sericins from the different species are examined for attachment, growth, proliferation, and morphology of fibrosarcoma cells. The optimum sericin supplementation seems to vary with the source of sericins. The results indicate that all the sericins promote the growth of L929 cells in serum-free culture media; however, S. ricini sericin seems to promote better growth of cells amongst other non-mulberry sericins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Purification and biochemical characterization of a 70 kDa sericin from tropical tasar silkworm, Antheraea mylitta.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 May;147(1):129-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Jan 30. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17350301
-
Silk gland sericin protein membranes: fabrication and characterization for potential biotechnological applications.J Biotechnol. 2009 Dec;144(4):321-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2009.09.019. Epub 2009 Oct 4. J Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19808068
-
Characteristics of silk fiber with and without sericin component: a comparison between Bombyx mori and Philosamia ricini silks.Pak J Biol Sci. 2009 Jun 1;12(11):872-6. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2009.872.876. Pak J Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19803122
-
Nonmulberry silk proteins: multipurpose ingredient in bio-functional assembly.Biomed Mater. 2021 Sep 22;16(6). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac20a0. Biomed Mater. 2021. PMID: 34428758 Review.
-
Chinese Oak Tasar Silkworm Antheraea pernyi Silk Proteins: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives for Biomedical Applications.Macromol Biosci. 2019 Mar;19(3):e1800252. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800252. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Macromol Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30294916 Review.
Cited by
-
Sericin from Fibroin-Deficient Silkworms Served as a Promising Resource for Biomedicine.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jul 4;15(13):2941. doi: 10.3390/polym15132941. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Silk-Fibroin-Based Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering.Gels. 2023 May 22;9(5):431. doi: 10.3390/gels9050431. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37233022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-functional bioactive silk sericin for osteoblast responses and osteomyelitis treatment.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 2;17(3):e0264795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264795. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35235612 Free PMC article.
-
Novel sericin-based hepatocyte serum-free medium and sericin's effect on hepatocyte transcriptome.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 14;24(30):3398-3413. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3398. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30122879 Free PMC article.
-
Silk Protein Composite Bioinks and Their 3D Scaffolds and In Vitro Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 14;23(2):910. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020910. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yanagihara K., Miki M., Ogawa A., Sasaki M., Yamada H., Terada S. Effects of sericin on promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis of mammalian cells. In: Shirahata S., Ikura K., Nagao M., Ichikawa A., Teruya K., editors. Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects. Vol. 15. 2009. pp. 31–36. (Animal Cell Technology: Basic & Applied Aspects). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

