MicroRNA-126 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting the chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and Ras homolog gene family, member A, signaling pathway
- PMID: 27517626
- PMCID: PMC5312381
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11176
MicroRNA-126 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting the chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and Ras homolog gene family, member A, signaling pathway
Abstract
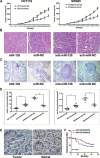
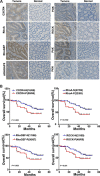
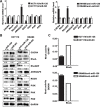
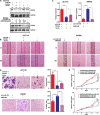
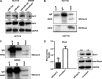
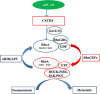
MicroRNA-126 (miR-126) suppresses the migration, proliferation and invasion of colon cancer cells. However, the underlying mechanisms of miR-126 in colon cancer have not been fully elucidated. In this study, in vivo experiments revealed that miR-126 inhibits colon cancer growth and metastasis. Furthermore, miR-126 was down-regulated in human colon cancer tissue, and its expression was inversely correlated with TNM stage and metastasis of patients. Low level of miR-126 identified patients with poor prognosis. And we found that miR-126 expression was negatively correlated with the expression levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) and components of signaling pathway of Ras homolog gene family, member A (RhoA) in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we verified that miR-126 negatively regulated CXCR4 and RhoA signaling in vitro. In addition, either in miR-126-overexpressing or in miR- 126-silenced colon cancer cells, the restoration of CXCR4 could significantly reverse the proliferation and invasion, as well as abolish the effects of miR-126 on RhoA signaling pathway. Collectively, these results demonstrated that miR-126 acts as a tumor suppressor by inactivating RhoA signaling via CXCR4 in colon cancer. And miR-126 may serve as a prognostic marker for monitoring and treating colon cancer.
Keywords: CXCR4; RhoA; colon cancer; microRNA-126 (mir-126).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
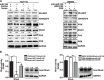
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-506 suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis in colon cancer by directly targeting the oncogene EZH2.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):32586-601. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5309. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26452129 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-31 inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting RhoA in human gastric cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Aug;38(2):1133-1139. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5758. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28656284
-
CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes inflammation-driven colorectal cancer progression through activation of RhoA signaling by sponging miR-133a-3p.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 24;38(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-1014-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30678736 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic potency of microRNA 21 in the pathogenesis of colon cancer, current status and prospective.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8075-8081. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27580. Epub 2018 Oct 14. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30317621 Review.
-
RHOA Therapeutic Targeting in Hematological Cancers.Cells. 2023 Jan 28;12(3):433. doi: 10.3390/cells12030433. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nickel's Role in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Potential Involvement of microRNAs.Toxics. 2022 Mar 21;10(3):148. doi: 10.3390/toxics10030148. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35324773 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA-210, miRNA-21 and miRNA-126 as diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal carcinoma: impact of HIF-1α-VEGF signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;454(1-2):177-189. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3462-1. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30357530
-
CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Target in Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7371. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147371. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of microRNA-126 relates to favorable prognosis for colon cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2021 May 5;11(1):9592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87985-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33953222 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL12 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1302:51-70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-62658-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34286441 Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:104–117. - PubMed
-
- Mulrane L, McGee SF, Gallagher WM, O'Connor DP. miRNA dysregulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:6554–6562. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–866. - PubMed
-
- Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR, Jacks T. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39:673–677. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

