Co-regulation of mRNA translation by TDP-43 and Fragile X Syndrome protein FMRP
- PMID: 27518042
- PMCID: PMC5073124
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-016-1603-8
Co-regulation of mRNA translation by TDP-43 and Fragile X Syndrome protein FMRP
Abstract
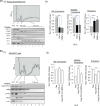
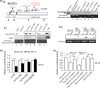
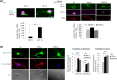
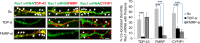
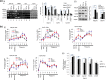
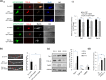
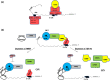
For proper mammalian brain development and functioning, the translation of many neuronal mRNAs needs to be repressed without neuronal activity stimulations. We have discovered that the expression of a subclass of neuronal proteins essential for neurodevelopment and neuron plasticity is co-regulated at the translational level by TDP-43 and the Fragile X Syndrome protein FMRP. Using molecular, cellular and imaging approaches, we show that these two RNA-binding proteins (RBP) co-repress the translation initiation of Rac1, Map1b and GluR1 mRNAs, and consequently the hippocampal spinogenesis. The co-repression occurs through binding of TDP-43 to mRNA(s) at specific UG/GU sequences and recruitment of the inhibitory CYFIP1-FMRP complex by its glycine-rich domain. This novel regulatory scenario could be utilized to silence a significant portion of around 160 common target mRNAs of the two RBPs. The study establishes a functional/physical partnership between FMRP and TDP-43 that mechanistically links several neurodevelopmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: CYFIP1; FISH; FMRP; Immunofluorescence staining; Live cell imaging; Polysome profile; RNA-IP; TDP-43; Translation initiation.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

