Early Endothelial Progenitor Cells (eEPCs) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) - dynamics of cellular regeneration and mesenchymal transdifferentiation
- PMID: 27519706
- PMCID: PMC4983068
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-016-1197-2
Early Endothelial Progenitor Cells (eEPCs) in systemic sclerosis (SSc) - dynamics of cellular regeneration and mesenchymal transdifferentiation
Abstract
Background: Patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) are endagered by tissue fibrosis and by microvasculopathy, with the latter caused by endothelial cell expansion/proliferation. SSc-associated fibrosis potentially results from mesenchymal transdifferentiation of endothelial cells. Early Endothelial Progenitor Cells (eEPCs) act proangiogenic under diverse conditions. Aim of the study was to analyze eEPC regeneration and mesenchymal transdifferentiation in patients with limited and diffuse SSs (lSSc and dSSc).
Methods: Patients with both, lSSc and dSSc were included into the study. The following parameters were evaluated: eEPC numbers and regeneration, concentrations of vasomodulatory mediators, mesenchymal properties of blood-derived eEPC. Serum samples of healthy subjects and SS patients were used for stimulation of cultured human eEPC, subsequently followed by analysis of mesenchymal cell characteristics and mobility.
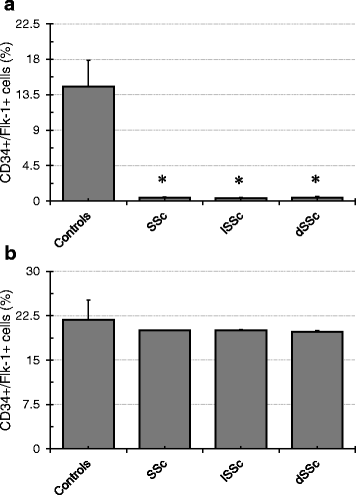
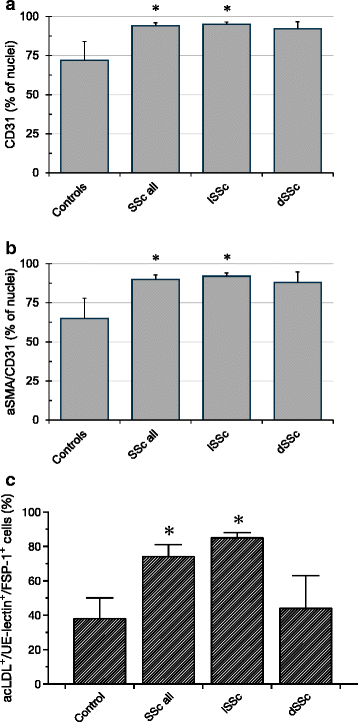
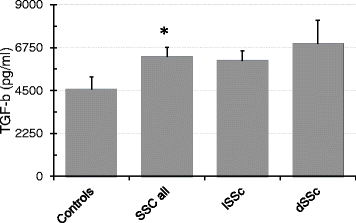
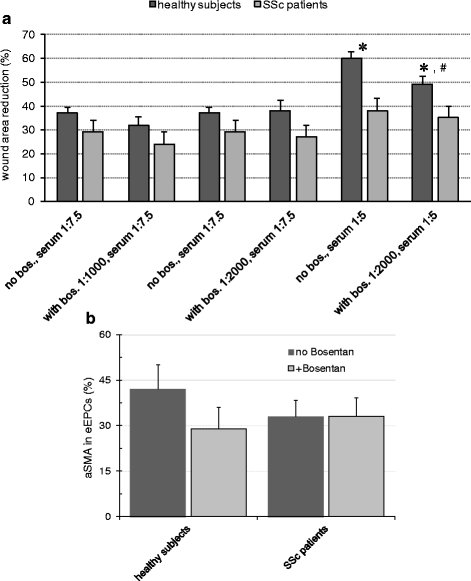
Results: Twenty-nine patients were included into the study. Regenerative activity of blood-derived eEPCs did not differ between Controls and patients. Circulating eEPC were significantly lower in all patients with SSc, and in limited and diffuse SSc (lSSc/dSSc). Serum concentrations of promesenchymal TGF-b was elevated in all patients with SSc. Cultured mononuclear cells from SS patients displayed higher abundances of CD31 and of CD31 and aSMA combined. Finally, serum from SSc patients inhibited migration of cultured eEPCs and the cells showed lower sensitivity towards the endothelin antagonist Bosentan.
Conclusions: The eEPC system, which represents an essential element of the endogenous vascular repair machinery is affected in SSc. The increased appearance of mesenchymal properties in eEPC may indicate that alterations of the cells potentially contribute to the accumulation of connective tissue and to vascular malfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum levels, tissue expression and cellular secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in limited and diffuse systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;33(4 Suppl 91):S98-105. Epub 2015 May 25. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26005773
-
Abnormal nitric oxide metabolism in systemic sclerosis: increased levels of nitrated proteins and asymmetric dimethylarginine.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Jun;45(6):676-84. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei276. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. PMID: 16399843
-
Damage of cutaneous peripheral nervous system evolves differently according to the disease phase and subset of systemic sclerosis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005 May;44(5):607-13. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh559. Epub 2005 Feb 22. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2005. PMID: 15728417
-
Endothelial autophagy and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EndoMT) in eEPC treatment of ischemic AKI.J Nephrol. 2016 Oct;29(5):637-44. doi: 10.1007/s40620-015-0222-0. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26289253 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum concentrations of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: association with severity of pulmonary fibrosis.J Rheumatol. 2010 Apr;37(4):787-91. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.090664. Epub 2010 Feb 15. J Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20156945
Cited by
-
Treatable Traits in Systemic Sclerosis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023 Oct;65(2):251-276. doi: 10.1007/s12016-023-08969-x. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37603199 Review.
-
The "myth" of loss of angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis: a pivotal early pathogenetic process or just a late unavoidable event?Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Jul 6;19(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1370-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28683836 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Endothelial Progenitors in the Repair of Vascular Damage in Systemic Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 18;9:1383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01383. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29967618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenic T Cells: Potential Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in Autoimmune Diseases?Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 5;10(4):851. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040851. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453601 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Progenitor Cells: Relevant Players in the Vasculopathy and Lung Fibrosis Associated with the Presence of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis Patients.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 20;9(7):847. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070847. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mowat A. Connective tissue diseases. Clin Haematol. 1972;1:573–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

