Activation of Liver X Receptor Attenuates Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 27520356
- PMCID: PMC5222979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.06.018
Activation of Liver X Receptor Attenuates Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
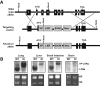
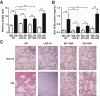
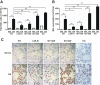
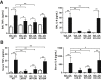
Liver X receptors (LXRs) were identified as receptors that sense oxidized cholesterol derivatives. LXRs are best known for their hepatic functions in regulating cholesterol metabolism and triglyceride synthesis, but whether and how LXRs play a role in the lung diseases is less understood. To study the function of LXRs in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), we applied the oleic acid (OA) model of ARDS to mice whose LXR was genetically or pharmacologically activated. The VP-LXRα knock-in (LXR-KI) mice, in which a constitutively activated LXRα (VP-LXRα) was inserted into the mouse LXRα locus, were used as the genetic gain-of-function model. We showed that the OA-induced lung damages, including the cytokine levels and total cell numbers and neutrophil numbers in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, the wet/dry weight ratio, and morphological abnormalities were reduced in the LXR-KI mice and wild-type mice treated with the LXR agonist GW3965. The pulmonoprotective effect of GW3965 was abolished in the LXR-null mice. Consistent with the pulmonoprotective effect of LXR and the induction of antioxidant enzymes by LXR, the OA-induced suppression of superoxide dismutase and catalase was attenuated in LXR-KI mice and GW3965-treated wild-type mice. Taken together, our results demonstrate that activation of LXRs can alleviate OA-induced ARDS by attenuating the inflammatory response and enhancing antioxidant capacity.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ashbaugh D.G., Bigelow D.B., Petty T.L., Levine B.E. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet. 1967;2:319–323. - PubMed
-
- Gordon D., Rubenfeld G.D., Caldwell E., Peabody E., Weaver J., Martin D.P., Neff M., Stern E.J., Hudson L.D. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1685–1693. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

