Management of Helicobacter pylori infections
- PMID: 27520775
- PMCID: PMC4983046
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-016-0496-2
Management of Helicobacter pylori infections
Abstract
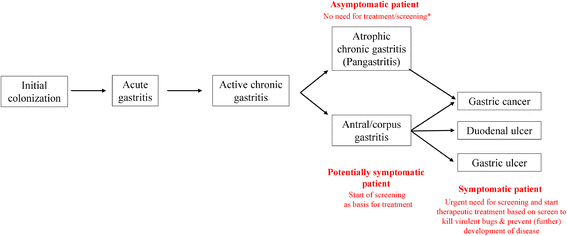
Background: Infection with Helicobacter pylori is associated with severe digestive diseases including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, and gastric cancer. Successful eradication of this common gastric pathogen in individual patients is known to prevent the occurrence of peptic ulcer disease and gastric cancer.
Discussion: With half of the world's population being infected with H, pylori and only few antibiotics result in an effective eradication, a successful antibiotic driven worldwide eradication program seems unlikely. In addition, H. pylori eradication is not always beneficial as it has been described that eradication can be associated with an increased frequency of other disorders such as pediatric asthma, inflammatory bowel diseases and Barrett's Esophagus. We have to accept that eradication of this infection is a two-edged sword that is both useful and harmful and we should therefore focus our H. pylori eradication policy toward selectively identify and destroy only the virulent strains.
Conclusion: In order to still be able to effectively treat H. pylori infections in the future we need an alternative diagnostic/treatment algorithm. This would involve a shift towards more precise and enhanced disease predicting diagnosis that tries to identify patients with chance of developing severe diseases such as gastric cancer, rather than the current regime that is geared towards find and destroy all H. pylori.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Eradication therapy; Gastric cancer; H. pylori.
Figures
References
-
- Nicolson GL, Haier J. Role of chronic bacterial and viral infections in neurodegenerative, neurobehavioural,psychiatric, autoimmune and fatiguing illnesses: part 2. Br J Med Pract. 2010;3(1):301–10.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

