Neurofilament light chain level is a weak risk factor for the development of MS
- PMID: 27521440
- PMCID: PMC5027802
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003085
Neurofilament light chain level is a weak risk factor for the development of MS
Erratum in
-
Neurofilament light chain level is a weak risk factor for the development of MS.Neurology. 2016 Nov 8;87(19):2068. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003368. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27821568 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To determine the prognostic value of selected biomarkers in clinically isolated syndromes (CIS) for conversion to multiple sclerosis (MS) and disability accrual.
Methods: Data were acquired from 2 CIS cohorts. The screening phase evaluated patients developing clinically definite MS (CIS-CDMS) and patients who remained as CIS during a 2-year minimum follow-up (CIS-CIS). We determined levels of neurofascin, semaphorin 3A, fetuin A, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and neurofilament light (NfL) and heavy chains in CSF (estimated mean [95% confidence interval; CI]). We evaluated associations between biomarker levels, conversion, disability, and magnetic resonance parameters. In the replication phase, we determined NfL levels (n = 155) using a 900 ng/L cutoff. Primary endpoints in uni- and multivariate analyses were CDMS and 2010 McDonald MS.
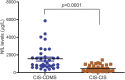
Results: The only biomarker showing significant differences in the screening was NfL (CIS-CDMS 1,553.1 [1,208.7-1,897.5] ng/L and CIS-CIS 499.0 [168.8-829.2] ng/L, p < 0.0001). The strongest associations were with brain parenchymal fraction change (rs = -0.892) and percentage brain volume change (rs = -0.842) at 5 years. NfL did not correlate with disability. In the replication phase, more NfL-positive patients, according to the cutoff, evolved to MS. Every 100-ng/L increase in NfL predicted CDMS (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.009, 95% CI 1.005-1.014) and McDonald MS (HR = 1.009, 95% CI 1.005-1.013), remaining significant for CDMS in the multivariate analysis (adjusted HR = 1.005, 95% CI 1.000-1.011). This risk was lower than the presence of oligoclonal bands or T2 lesions.
Conclusions: NfL is a weak independent risk factor for MS. Its role as an axonal damage biomarker may be more relevant as suggested by its association with medium-term brain volume changes.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
CSF neurofilament light: A universal risk biomarker in multiple sclerosis?Neurology. 2016 Sep 13;87(11):1068-9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003107. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27521432 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fisniku LK, Brex PA, Altmann DR, et al. . Disability and T2 MRI lesions: a 20-year follow-up of patients with relapse onset of multiple sclerosis. Brain 2008;131:808–817. - PubMed
-
- Tintore M, Rovira A, Rio J, et al. . Do oligoclonal bands add information to MRI in first attacks of multiple sclerosis? Neurology 2008;70:1079–1083. - PubMed
-
- Masjuan J, Alvarez-Cermeno JC, Garcia-Barragan N, et al. . Clinically isolated syndromes: a new oligoclonal band test accurately predicts conversion to MS. Neurology 2006;66:576–578. - PubMed
-
- Comabella M, Montalban X. Body fluid biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2014;13:113–126. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
