Multifaceted biological insights from a draft genome sequence of the tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta
- PMID: 27522922
- PMCID: PMC5010457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.07.005
Multifaceted biological insights from a draft genome sequence of the tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta
Abstract
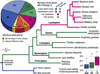
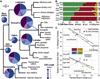
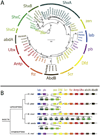
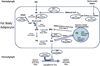
Manduca sexta, known as the tobacco hornworm or Carolina sphinx moth, is a lepidopteran insect that is used extensively as a model system for research in insect biochemistry, physiology, neurobiology, development, and immunity. One important benefit of this species as an experimental model is its extremely large size, reaching more than 10 g in the larval stage. M. sexta larvae feed on solanaceous plants and thus must tolerate a substantial challenge from plant allelochemicals, including nicotine. We report the sequence and annotation of the M. sexta genome, and a survey of gene expression in various tissues and developmental stages. The Msex_1.0 genome assembly resulted in a total genome size of 419.4 Mbp. Repetitive sequences accounted for 25.8% of the assembled genome. The official gene set is comprised of 15,451 protein-coding genes, of which 2498 were manually curated. Extensive RNA-seq data from many tissues and developmental stages were used to improve gene models and for insights into gene expression patterns. Genome wide synteny analysis indicated a high level of macrosynteny in the Lepidoptera. Annotation and analyses were carried out for gene families involved in a wide spectrum of biological processes, including apoptosis, vacuole sorting, growth and development, structures of exoskeleton, egg shells, and muscle, vision, chemosensation, ion channels, signal transduction, neuropeptide signaling, neurotransmitter synthesis and transport, nicotine tolerance, lipid metabolism, and immunity. This genome sequence, annotation, and analysis provide an important new resource from a well-studied model insect species and will facilitate further biochemical and mechanistic experimental studies of many biological systems in insects.
Keywords: Innate immunity; Insect; Insect biochemistry; Lepidoptera; Moth; Synteny; Tobacco hornworm.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Integrated modeling of protein-coding genes in the Manduca sexta genome using RNA-Seq data from the biochemical model insect.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;62:2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25612938 Free PMC article.
-
De novo genome assembly of the tobacco hornworm moth (Manduca sexta).G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jan 18;11(1):jkaa047. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaa047. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33561252 Free PMC article.
-
An analysis of 67 RNA-seq datasets from various tissues at different stages of a model insect, Manduca sexta.BMC Genomics. 2017 Oct 17;18(1):796. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4147-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29041902 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental expression of mRNAs for epidermal and fat body proteins and hormonally regulated transcription factors in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta.J Insect Physiol. 2010 Oct;56(10):1390-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.03.029. Epub 2010 Apr 7. J Insect Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20361974 Review.
-
Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Dec;33(12):1327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2003.06.001. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14599504 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic structure and insecticide resistance characteristics of fall armyworm populations invading China.Mol Ecol Resour. 2020 Nov;20(6):1682-1696. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13219. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020. PMID: 32619331 Free PMC article.
-
Cotesia congregata Bracovirus Circles Encoding PTP and Ankyrin Genes Integrate into the DNA of Parasitized Manduca sexta Hemocytes.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00438-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00438-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769342 Free PMC article.
-
Serpin-9 and -13 regulate hemolymph proteases during immune responses of Manduca sexta.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Nov;90:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.09.015. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28987647 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the evolution of a color polyphenism by genetic accommodation in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 25;122(12):e2425004122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2425004122. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40106356
-
Morphological and Transcriptomic Analysis of a Beetle Chemosensory System Reveals a Gnathal Olfactory Center.BMC Biol. 2016 Oct 17;14(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0304-z. BMC Biol. 2016. PMID: 27751175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad SA, Hopkins TL. Beta-glucosylation of plant phenolics by phenol beta-glucosyltransferase in larval tissues of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L) Insect Bioch. Mol. Biol. 1993a;23:581–589.
-
- Ahmad SA, Hopkins TL. Phenol beta-glucosyltransferases in 6 species of insects – properties and tissue Localization. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B. 1993b;104:515–519.
-
- Ahmad SA, Hopkins TL, Kramer KJ. Tyrosine beta-glucosyltransferase in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L): properties, tissue localization, and developmental profile. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996;26:49–57.
-
- Ahn SJ, Vogel H, Heckel DG. Comparative analysis of the UDP-glycosyltransferase multigene family in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012;42:133–147. - PubMed
-
- Ahola V, Lehtonen R, Somervuo P, Salmela L, Koskinen P, Rastas P, Valimaki N, Paulin L, Kvist J, Wahlberg N, Tanskanen J, Hornett EA, Ferguson LC, Luo S, Cao Z, de Jong MA, Duplouy A, Smolander OP, Vogel H, McCoy RC, Qian K, Chong WS, Zhang Q, Ahmad E, Haukka JK, Joshi A, Salojarvi J, Wheat CW, Grosse-Wilde E, Hughes D, Katainen R, Pitkanen E, Ylinen J, Waterhouse RM, Turunen M, Vaharautio A, Ojanen SP, Schulman AH, Taipale M, Lawson D, Ukkonen E, Makinen V, Goldsmith MR, Holm L, Auvinen P, Frilander MJ, Hanski I. The Glanville fritillary genome retains an ancient karyotype and reveals selective chromosomal fusions in Lepidoptera. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4737. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

