The Deubiquitinase OTULIN Is an Essential Negative Regulator of Inflammation and Autoimmunity
- PMID: 27523608
- PMCID: PMC5002269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.019
The Deubiquitinase OTULIN Is an Essential Negative Regulator of Inflammation and Autoimmunity
Abstract
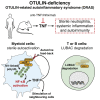
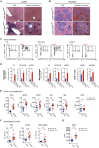
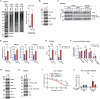
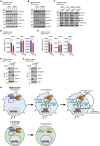
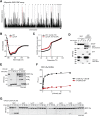
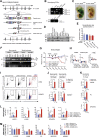
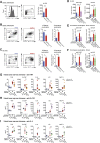
Methionine-1 (M1)-linked ubiquitin chains regulate the activity of NF-κB, immune homeostasis, and responses to infection. The importance of negative regulators of M1-linked chains in vivo remains poorly understood. Here, we show that the M1-specific deubiquitinase OTULIN is essential for preventing TNF-associated systemic inflammation in humans and mice. A homozygous hypomorphic mutation in human OTULIN causes a potentially fatal autoinflammatory condition termed OTULIN-related autoinflammatory syndrome (ORAS). Four independent OTULIN mouse models reveal that OTULIN deficiency in immune cells results in cell-type-specific effects, ranging from over-production of inflammatory cytokines and autoimmunity due to accumulation of M1-linked polyubiquitin and spontaneous NF-κB activation in myeloid cells to downregulation of M1-polyubiquitin signaling by degradation of LUBAC in B and T cells. Remarkably, treatment with anti-TNF neutralizing antibodies ameliorates inflammation in ORAS patients and rescues mouse phenotypes. Hence, OTULIN is critical for restraining life-threatening spontaneous inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bonizzi G., Karin M. The two NF-kappaB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Clark G.R., Sciacovelli M., Gaude E., Walsh D.M., Kirby G., Simpson M.A., Trembath R.C., Berg J.N., Woodward E.R., Kinning E. Germline FH mutations presenting with pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014;99:E2046–E2050. - PubMed
-
- Clausen B.E., Burkhardt C., Reith W., Renkawitz R., Förster I. Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysMcre mice. Transgenic Res. 1999;8:265–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

