Endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasias caused by mutations in collagen types II and X
- PMID: 27523816
- PMCID: PMC5083666
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-016-0719-z
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasias caused by mutations in collagen types II and X
Abstract
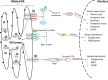
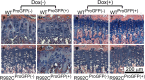
The endoplasmic reticulum is primarily recognized as the site of synthesis and folding of secreted, membrane-bound, and some organelle-targeted proteins. An imbalance between the load of unfolded proteins and the processing capacity in endoplasmic reticulum leads to the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum stress, which is a hallmark of a number of storage diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, a number of metabolic diseases, and cancer. Moreover, its contribution as a novel mechanistic paradigm in genetic skeletal diseases associated with abnormalities of the growth plates and dwarfism is considered. In this review, I discuss the mechanistic significance of endoplasmic reticulum stress, abnormal folding, and intracellular retention of mutant collagen types II and X in certain variants of skeletal chondrodysplasia.
Keywords: Chondrodysplasia; Collagen; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Mechanism; Mutation; Unfolded protein response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differentiation of Hypertrophic Chondrocytes from Human iPSCs for the In Vitro Modeling of Chondrodysplasias.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Mar 9;16(3):610-625. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.014. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 33636111 Free PMC article.
-
Increased classical endoplasmic reticulum stress is sufficient to reduce chondrocyte proliferation rate in the growth plate and decrease bone growth.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 18;10(2):e0117016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117016. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25693198 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress induces cartilage pathology.PLoS Genet. 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000691. Epub 2009 Oct 16. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19834559 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Cartilage Pathophysiology; Contributing Factors to Apoptosis and Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 20;18(3):665. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030665. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28335520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and models of endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasia.Dev Dyn. 2014 Jul;243(7):875-93. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24131. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Dev Dyn. 2014. PMID: 24668528 Review.
Cited by
-
4-PBA ameliorates cellular homeostasis in fibroblasts from osteogenesis imperfecta patients by enhancing autophagy and stimulating protein secretion.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 May;1864(5 Pt A):1642-1652. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.02.002. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29432813 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Mediated Endogenous Activation of Fibroin Heavy Chain Gene Triggers Cellular Stress Responses in Bombyx mori Embryonic Cells.Insects. 2021 Jun 13;12(6):552. doi: 10.3390/insects12060552. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34199296 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressing UPR-dependent overactivation of FGFR3 signaling ameliorates SLC26A2-deficient chondrodysplasias.EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:695-709. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Jan 23. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30685387 Free PMC article.
-
Maturation of the equine medial femoral condyle osteochondral unit.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2020 Jan 27;2(1):100029. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2020.100029. eCollection 2020 Mar. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2020. PMID: 36474556 Free PMC article.
-
Different Forms of ER Stress in Chondrocytes Result in Short Stature Disorders and Degenerative Cartilage Diseases: New Insights by Cartilage-Specific ERp57 Knockout Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Dec 17;2018:8421394. doi: 10.1155/2018/8421394. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30647818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ang A, Ung T, Puvanachandra N, Wilson L, Howard F, Ryalls M, Richards A, Meredith S, Laidlaw M, Poulson A, Scott J, Snead M. Vitreous phenotype: a key diagnostic sign in Stickler syndrome types 1 and 2 complicated by double heterozygosity. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A(6):604–607. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31527. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arita M, Fertala J, Hou C, Steplewski A, Fertala A. Mechanisms of aberrant organization of growth plates in conditional transgenic mouse model of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia associated with the R992C substitution in collagen II. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(1):214–229. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.09.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

