Change in the Molecular Dimension of a RAGE-Ligand Complex Triggers RAGE Signaling
- PMID: 27524199
- PMCID: PMC5014727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2016.06.021
Change in the Molecular Dimension of a RAGE-Ligand Complex Triggers RAGE Signaling
Abstract
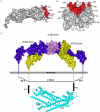
The weak oligomerization exhibited by many transmembrane receptors has a profound effect on signal transduction. The phenomenon is difficult to characterize structurally due to the large sizes of and transient interactions between monomers. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), a signaling molecule central to the induction and perpetuation of inflammatory responses, is a weak constitutive oligomer. The RAGE domain interaction surfaces that mediate homo-dimerization were identified by combining segmental isotopic labeling of extracellular soluble RAGE (sRAGE) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry. Molecular modeling suggests that two sRAGE monomers orient head to head forming an asymmetric dimer with the C termini directed toward the cell membrane. Ligand-induced association of RAGE homo-dimers on the cell surface increases the molecular dimension of the receptor, recruiting Diaphanous 1 (DIAPH1) and activating signaling pathways.
Keywords: NMR spectroscopy; RAGE; cancer; diabetes; diaphanous 1; hybrid method of structure determination; inflammation; mass spectrometry; pattern recognition; receptor for advanced glycation end products; segmental labeling; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycation & the RAGE axis: targeting signal transduction through DIAPH1.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Feb;14(2):147-156. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1271719. Epub 2016 Dec 22. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27967251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pentamidine blocks the interaction between mutant S100A5 and RAGE V domain and inhibits the RAGE signaling pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Aug 19;477(2):188-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.041. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27297108
-
Blocking the Interactions between Calcium-Bound S100A12 Protein and the V Domain of RAGE Using Tranilast.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 6;11(9):e0162000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162000. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27598566 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Inhibition of Ligand-Stimulated RAGE-DIAPH1 Signal Transduction.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 3;6:22450. doi: 10.1038/srep22450. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26936329 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Diversity of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products.Acta Med Okayama. 2017 Dec;71(6):459-465. doi: 10.18926/AMO/55582. Acta Med Okayama. 2017. PMID: 29276218 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Homophilic Interactions and Ligand Binding of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products by Heparin and Heparin-Related Carbohydrate Structures.Medicines (Basel). 2018 Jul 30;5(3):79. doi: 10.3390/medicines5030079. Medicines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30061484 Free PMC article.
-
DIAPH1-MFN2 interaction regulates mitochondria-SR/ER contact and modulates ischemic/hypoxic stress.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 30;14(1):6900. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42521-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37903764 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) and Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Insights From Human Subjects and Animal Models.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Mar 10;7:37. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00037. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32211423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAGE Signaling in Melanoma Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8989. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238989. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAGE/DIAPH1 and atherosclerosis through an evolving lens: Viewing the cell from the "Inside - Out".Atherosclerosis. 2024 Jul;394:117304. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.117304. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Atherosclerosis. 2024. PMID: 39131441 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angers S, Salahpour A, Bouvier M. Dimerization: an emerging concept for G protein-coupled receptor ontogeny and function. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology. 2002;42:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Bernado P, Garcia de la Torre J, Pons M. Interpretation of 15N NMR relaxation data of globular proteins using hydrodynamic calculations with HYDRONMR. J Biomol NMR. 2002;23:139–150. - PubMed
-
- Berry R, Chen Z, McCluskey J, Rossjohn J. Insight into the basis of autonomous immunoreceptor activation. Trends in immunology. 2011;32:165–170. - PubMed
-
- Blobel J, Bernado P, Xu H, Jin C, Pons M. Weak oligomerization of low-molecular-weight protein tyrosine phosphatase is conserved from mammals to bacteria. The FEBS journal. 2009;276:4346–4357. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

