Proximity-Based Differential Single-Cell Analysis of the Niche to Identify Stem/Progenitor Cell Regulators
- PMID: 27524439
- PMCID: PMC5402355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.07.004
Proximity-Based Differential Single-Cell Analysis of the Niche to Identify Stem/Progenitor Cell Regulators
Abstract
Physiological stem cell function is regulated by secreted factors produced by niche cells. In this study, we describe an unbiased approach based on the differential single-cell gene expression analysis of mesenchymal osteolineage cells close to, and further removed from, hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) to identify candidate niche factors. Mesenchymal cells displayed distinct molecular profiles based on their relative location. We functionally examined, among the genes that were preferentially expressed in proximal cells, three secreted or cell-surface molecules not previously connected to HSPC biology-the secreted RNase angiogenin, the cytokine IL18, and the adhesion molecule Embigin-and discovered that all of these factors are HSPC quiescence regulators. Therefore, our proximity-based differential single-cell approach reveals molecular heterogeneity within niche cells and can be used to identify novel extrinsic stem/progenitor cell regulators. Similar approaches could also be applied to other stem cell/niche pairs to advance the understanding of microenvironmental regulation of stem cell function.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
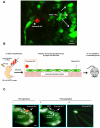




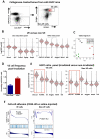
Comment in
-
Angiogenin Defines Heterogeneity at the Core of the Hematopoietic Niche.Cell Stem Cell. 2016 Sep 1;19(3):284-6. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.08.017. Cell Stem Cell. 2016. PMID: 27588743
References
-
- Adams GB, Martin RP, Alley IR, Chabner KT, Cohen KS, Calvi LM, Kronenberg HM, Scadden DT. Therapeutic targeting of a stem cell niche. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:238–243. - PubMed
-
- Bruscia EM, Ziegler EC, Price JE, Weiner S, Egan ME, Krause DS. Engraftment of donor-derived epithelial cells in multiple organs following bone marrow transplantation into newborn mice. Stem cells. 2006;24:2299–2308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K25 AG037596/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL087735/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL131477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL128127/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB014703/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HL096372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065237/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105241/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 11831/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 DK107784/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

