POLD3 Is Haploinsufficient for DNA Replication in Mice
- PMID: 27524497
- PMCID: PMC5029548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.007
POLD3 Is Haploinsufficient for DNA Replication in Mice
Abstract
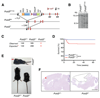
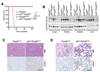
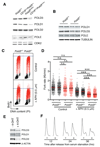
The Pold3 gene encodes a subunit of the Polδ DNA polymerase complex. Pold3 orthologs are not essential in Saccharomyces cerevisiae or chicken DT40 cells, but the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ortholog is essential. POLD3 also has a specialized role in the repair of broken replication forks, suggesting that POLD3 activity could be particularly relevant for cancer cells enduring high levels of DNA replication stress. We report here that POLD3 is essential for mouse development and is also required for viability in adult animals. Strikingly, even Pold3(+/-) mice were born at sub-Mendelian ratios, and, of those born, some presented hydrocephaly and had a reduced lifespan. In cells, POLD3 deficiency led to replication stress and cell death, which were aggravated by the expression of activated oncogenes. Finally, we show that Pold3 deletion destabilizes all members of the Polδ complex, explaining its major role in DNA replication and the severe impact of its deficiency.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The POLD3 subunit of DNA polymerase δ can promote translesion synthesis independently of DNA polymerase ζ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 18;43(3):1671-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv023. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25628356 Free PMC article.
-
Pold4 is dispensable for mouse development, DNA replication and DNA repair.Gene. 2023 Jan 30;851:147029. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.147029. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Gene. 2023. PMID: 36356905
-
In vivo evidence for translesion synthesis by the replicative DNA polymerase δ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 6;44(15):7242-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw439. Epub 2016 May 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27185888 Free PMC article.
-
POLD3 as Controller of Replicative DNA Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 19;25(22):12417. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212417. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
POLD1: Central mediator of DNA replication and repair, and implication in cancer and other pathologies.Gene. 2016 Sep 15;590(1):128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.06.031. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27320729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Break-induced telomere synthesis underlies alternative telomere maintenance.Nature. 2016 Nov 3;539(7627):54-58. doi: 10.1038/nature20099. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27760120 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerase delta interacting protein 3 facilitates the activation and maintenance of DNA damage checkpoint in response to replication stress.Animal Model Exp Med. 2022 Oct;5(5):461-469. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12274. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Animal Model Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36168146 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian RAD52 Functions in Break-Induced Replication Repair of Collapsed DNA Replication Forks.Mol Cell. 2016 Dec 15;64(6):1127-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.10.038. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27984746 Free PMC article.
-
The stabilized Pol31-Pol3 interface counteracts Pol32 ablation with differential effects on repair.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Jul 5;4(9):e202101138. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101138. Print 2021 Sep. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34226278 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the ghost proteome in ovarian cancer cells by deep proteogenomic characterization.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Sep 30;15(9):712. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07046-1. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39349928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ducoux M, Urbach S, Baldacci G, Hubscher U, Koundrioukoff S, Christensen J, Hughes P. Mediation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-dependent DNA replication through a conserved p21(Cip1)-like PCNA-binding motif present in the third subunit of human DNA polymerase delta. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:49258–49266. - PubMed
-
- Gerik KJ, Li X, Pautz A, Burgers PM. Characterization of the two small subunits of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA polymerase delta. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19747–19755. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

