Comparison of the Effects of Glutamine, Curcumin, and Nesfatin-1 on the Gastric Serosal Surface Neomucosa Formation: An Experimental Rodent Model
- PMID: 27525002
- PMCID: PMC4972927
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2081962
Comparison of the Effects of Glutamine, Curcumin, and Nesfatin-1 on the Gastric Serosal Surface Neomucosa Formation: An Experimental Rodent Model
Abstract
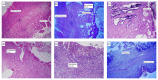
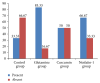
Introduction. Short bowel syndrome can crop up if more than 50% of small intestine is resected or when less than 100 cm of small bowel is left. Glutamine is the main food source of enterocytes. Curcumin has protective effects on intestinal ischemia-reperfusion damage. Nesfatin-1 is a satiety molecule. It has protective effects on gastric mucosa. The primary purpose of this study is to compare effects of glutamine, curcumin, and nesfatin-1 on the gastric serosal surface neomucosa formation on rats. Materials and Methods. 24 Wistar-Hannover rats were randomly divided into 4 groups and treated with saline, glutamine, curcumin, and nesfatin-1 after ileogastric anastomosis. After 14 days all rats were euthanized, and blood was collected. En bloc resection of anastomotic part was performed for histopathological examination. Results. PDGF, TGF-β, and VEGF levels and neomucosa formation were higher in glutamine group (p = 0.003, p = 0.003, and p = 0.025). Glutamine promotes the intestinal neomucosa formation on the gastric serosal surface and augments growth factors essential for neomucosa formation on rats. Conclusion. Glutamine may be used in short bowel syndrome for increasing the absorption surface area. But that needs to be determined by adequately powered clinical trials.
Figures

References
-
- Wilhelm S. M., Lipari M., Kulik J. K., Kale-Pradhan P. B. Teduglutide for the treatment of short bowel syndrome. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2014;48(9):1209–1213. - PubMed
-
- Semrad C. E. Goldman's Cecil Medicine. 24th. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012. Approach to the patient with diarrhea and malabsorption; pp. 895–913.
-
- Godoy B. Z., Faintuch J., Marin M. L., Nogueira M. A., Pinto V. B., Pollara W. M. Off label pharmacological therapy in patients with short bowel syndrome. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2013;17(24):3285–3290. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

