Epigenetic features of FoxP3 in children with cow's milk allergy
- PMID: 27525046
- PMCID: PMC4981981
- DOI: 10.1186/s13148-016-0252-z
Epigenetic features of FoxP3 in children with cow's milk allergy
Abstract
Background: DNA methylation of the Th1 and Th2 cytokine genes is altered during cow's milk allergy (CMA). Forkhead box transcription factor 3 (FoxP3) is essential for the development and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and is involved in oral tolerance acquisition. We assessed whether tolerance acquisition in children with IgE-mediated CMA is associated with DNA demethylation of the Treg-specific demethylated region (TSDR) of FoxP3.
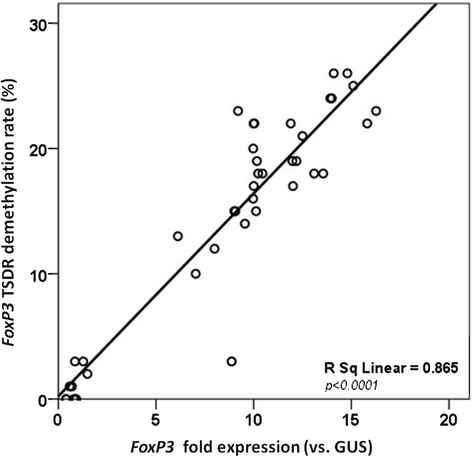
Results: Forty children (aged 3-18 months) were enrolled: 10 children with active IgE-mediated CMA (group 1), 10 children who outgrew CMA after dietary treatment with an extensively hydrolyzed casein formula containing the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (group 2), 10 children who outgrew CMA after treatment with other formulas (group 3), and 10 healthy controls (group 4). FoxP3 TSDR demethylation and expression were measured in mononuclear cells purified from peripheral blood of the four groups of children. FoxP3 TSDR demethylation was significantly lower in children with active IgE-mediated CMA than in either children who outgrew CMA or in healthy children. Formula selection influenced the FoxP3 TSDR demethylation profile. The FoxP3 TSDR demethylation rate and expression level were correlated.
Conclusions: Tolerance acquisition in children with IgE-mediated CMA involves epigenetic regulation of the FoxP3 gene. This feature could be a new target for preventive and therapeutic strategies against CMA.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02779881.
Keywords: Extensively hydrolyzed casein formula; Food allergy; Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; Oral tolerance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tolerogenic Effect Elicited by Protein Fraction Derived From Different Formulas for Dietary Treatment of Cow's Milk Allergy in Human Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 12;11:604075. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604075. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679694 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized controlled trial on the influence of dietary intervention on epigenetic mechanisms in children with cow's milk allergy: the EPICMA study.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 26;9(1):2828. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38738-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30808949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Formula selection for management of children with cow's milk allergy influences the rate of acquisition of tolerance: a prospective multicenter study.J Pediatr. 2013 Sep;163(3):771-7.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23582142 Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotics, prebiotics and food allergy: a review.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 May;56(3):99-110. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.319. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38054607 Review.
-
Hydrolyzed rice formula for dietary management of infants with cow's milk allergy.World Allergy Organ J. 2022 Nov 17;15(12):100717. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2022.100717. eCollection 2022 Dec. World Allergy Organ J. 2022. PMID: 36438193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Diet Diversity and Diet Indices on Allergy Outcomes.Front Pediatr. 2020 Sep 15;8:545. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00545. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33042906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal and Early-Life Nutrition, Epigenetics, and Allergy.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 25;13(3):724. doi: 10.3390/nu13030724. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33668787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive Effects of a Human Hematopoietic Mesenchymal Stem Cell (hHMSC) Therapy in Ovalbumin-Induced Food Allergy.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 21;10(2):511. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020511. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203718 Free PMC article.
-
The current state of omics technologies in the clinical management of asthma and allergic diseases.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019 Dec;123(6):550-557. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.08.460. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31494234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory T Cell Plasticity and Stability and Autoimmune Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020 Feb;58(1):52-70. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8721-0. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 30449014 Review.
References
-
- Berni Canani R, Paparo L, Nocerino R, Cosenza L, Pezzella V, Di Costanzo M, Capasso M, Del Monaco V, D’Argenio V, Greco L, Salvatore F. Differences in DNA methylation profile of Th1 and Th2 cytokine genes are associated with tolerance acquisition in children with IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy. Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:38. doi: 10.1186/s13148-015-0070-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

