Primary malignant myelomatous pleural effusion
- PMID: 27525090
- PMCID: PMC4974434
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.634
Primary malignant myelomatous pleural effusion
Abstract
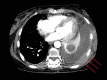
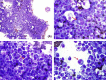
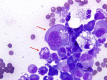
Primary malignant myelomatous pleural effusion (PMMPE) occurs in less than 1% of patients with multiple myeloma and is diagnosed either by visualization of plasma cells on cytology or by positive flow cytometry. The presence of immature plasma cells characterized by high nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, visible nucleolus and presence of Mott cells and Russell bodies are independent poor prognostic factors. The clinician should differentiate PMMPE from secondary pleural effusion as it is associated with a significantly worse prognosis and poor overall survival.
Keywords: Mott cells; Russell bodies; multiple myeloma; pleural effusion.
Figures
References
-
- Kamble, R. , Wilson C. S., Fassas A., Desikan R., Siegel D. S., Tricot G., et al. 2005. Malignant pleural effusion of multiple myeloma: prognostic factors and outcome. Leuk. Lymphoma 46:1137–1142. - PubMed
-
- Kintzer, J. S. , Rosenow E. C., and Kyle R. A.. 1978. Thoracic and pulmonary abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Arch. Intern. Med. 138:727–730. - PubMed
-
- Sawyer, J. R. 2011. The prognostic significance of cytogenetics and molecular profiling in multiple myeloma. Cancer Genet. 204:3–12. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

