Medical Internet of Things and Big Data in Healthcare
- PMID: 27525156
- PMCID: PMC4981575
- DOI: 10.4258/hir.2016.22.3.156
Medical Internet of Things and Big Data in Healthcare
Abstract
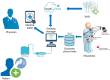
Objectives: A number of technologies can reduce overall costs for the prevention or management of chronic illnesses. These include devices that constantly monitor health indicators, devices that auto-administer therapies, or devices that track real-time health data when a patient self-administers a therapy. Because they have increased access to high-speed Internet and smartphones, many patients have started to use mobile applications (apps) to manage various health needs. These devices and mobile apps are now increasingly used and integrated with telemedicine and telehealth via the medical Internet of Things (mIoT). This paper reviews mIoT and big data in healthcare fields.
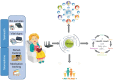
Methods: mIoT is a critical piece of the digital transformation of healthcare, as it allows new business models to emerge and enables changes in work processes, productivity improvements, cost containment and enhanced customer experiences.
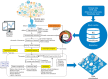
Results: Wearables and mobile apps today support fitness, health education, symptom tracking, and collaborative disease management and care coordination. All those platform analytics can raise the relevancy of data interpretations, reducing the amount of time that end users spend piecing together data outputs. Insights gained from big data analysis will drive the digital disruption of the healthcare world, business processes and real-time decision-making.
Conclusions: A new category of "personalised preventative health coaches" (Digital Health Advisors) will emerge. These workers will possess the skills and the ability to interpret and understand health and well-being data. They will help their clients avoid chronic and diet-related illness, improve cognitive function, achieve improved mental health and achieve improved lifestyles overall. As the global population ages, such roles will become increasingly important.
Keywords: Disease Management; Mobile Applications; Smartphone; Telemedicine; Wireless Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zanella A, Bui N, Castellani A, Vangelista L, Zorzi M. Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014;1(1):22–32.
-
- Bauer H, Patel M, Veira J. The Internet of Things: sizing up the opportunity [Internet] New York (NY): McKinsey & Company; c2016. [cited at 2016 Jul 1]. Available from: http://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/the-internet-o....
-
- Scheen AJ. Precision medicine: the future in diabetes care? Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;117:12–21. - PubMed
-
- van Leeuwen N, Swen JJ, Guchelaar HJ, 't Hart LM. The role of pharmacogenetics in drug disposition and response of oral glucose-lowering drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013;52(10):833–854. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

