Urea impairs β cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 27525435
- PMCID: PMC5004963
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI86181
Urea impairs β cell glycolysis and insulin secretion in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
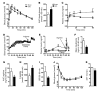
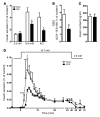
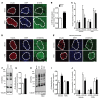
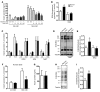
Disorders of glucose homeostasis are common in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and are associated with increased mortality, but the mechanisms of impaired insulin secretion in this disease remain unclear. Here, we tested the hypothesis that defective insulin secretion in CKD is caused by a direct effect of urea on pancreatic β cells. In a murine model in which CKD is induced by 5/6 nephrectomy (CKD mice), we observed defects in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in vivo and in isolated islets. Similarly, insulin secretion was impaired in normal mouse and human islets that were cultured with disease-relevant concentrations of urea and in islets from normal mice treated orally with urea for 3 weeks. In CKD mouse islets as well as urea-exposed normal islets, we observed an increase in oxidative stress and protein O-GlcNAcylation. Protein O-GlcNAcylation was also observed in pancreatic sections from CKD patients. Impairment of insulin secretion in both CKD mouse and urea-exposed islets was associated with reduced glucose utilization and activity of phosphofructokinase 1 (PFK-1), which could be reversed by inhibiting O-GlcNAcylation. Inhibition of O-GlcNAcylation also restored insulin secretion in both mouse models. These results suggest that insulin secretory defects associated with CKD arise from elevated circulating levels of urea that increase islet protein O-GlcNAcylation and impair glycolysis.
Figures



Comment in
-
Diabetes: Urea inhibits insulin secretion in CKD.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Oct;12(10):581. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.131. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27573727 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A role for PFK-2/FBPase-2, as distinct from fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, in regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells.Biochem J. 2008 Apr 1;411(1):41-51. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070962. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18039179
-
The effect of starvation on insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in mouse pancreatic islets.Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):423-33. doi: 10.1042/bj1400423. Biochem J. 1974. PMID: 4155624 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of insulin secretory function in two mouse models with different susceptibility to beta-cell failure.Endocrinology. 2002 Jun;143(6):2085-92. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.6.8859. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12021173
-
Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion.Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):163-214. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020301. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986. PMID: 2943567 Review. No abstract available.
-
Insulin secretion from beta cells within intact islets: location matters.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Apr;42(4):406-14. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12368. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25676261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Searching for Metabolic Markers of Stroke in Human Plasma via NMR Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 10;24(22):16173. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003362 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Patterns and Assessment of Long-term Complications followi ngSARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination in the Context of Diabet esPrevalence among Blood Donors.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(9):e110124225520. doi: 10.2174/0115733998274390231110050809. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024. PMID: 38415496
-
Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of T2DM in Chinese premenopausal and postmenopausal women.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Jul 17;18(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1091-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31315681 Free PMC article.
-
A low aromatic amino-acid diet improves renal function and prevent kidney fibrosis in mice with chronic kidney disease.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 28;11(1):19184. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98718-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34584168 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of insulin resistance in a rat model of kidney disease and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.PLoS One. 2017 May 1;12(5):e0176650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176650. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28459862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eldin WS, Ragheb A, Klassen J, Shoker A. Evidence for increased risk of prediabetes in the uremic patient. Nephron Clin Pract. 2008;108(1):c47–c55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

