Paraprotein-Related Kidney Disease: Evaluation and Treatment of Myeloma Cast Nephropathy
- PMID: 27526708
- PMCID: PMC5142056
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01640216
Paraprotein-Related Kidney Disease: Evaluation and Treatment of Myeloma Cast Nephropathy
Abstract
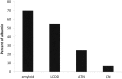
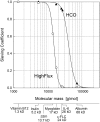
Nearly 50% of patients with multiple myeloma develop renal disease, most commonly from AKI caused by cast nephropathy. Development of AKI is associated with poor 1-year survival and reduces the therapeutic options available to patients. There is a great need for more effective therapies. Cast nephropathy is caused by the interaction and aggregation of filtered free light chains and Tamm-Horsfall protein causing intratubular obstruction and damage. The key to treating cast nephropathy is rapid lowering of free light chains, because this correlates with renal recovery. Newer chemotherapy agents rapidly lower free light chains and have been referred to as renoprotective. There is additional great interest in using extracorporeal therapies to remove serum free light chains. Small trials initially showed benefit of therapeutic plasma exchange to improve renal outcomes in cast nephropathy, but a large randomized trial of therapeutic plasma exchange failed to show benefit. A newer technique is extended high-cutoff hemodialysis. This modality uses a high molecular weight cutoff filter to remove free light chains. To date, trials of high-cutoff hemodialysis use in patients with cast nephropathy have been encouraging. However, there are no randomized trials showing the benefit of high-cutoff hemodialysis when used in addition to newer chemotherapeutic regimens. Until these studies are available, high-cutoff hemodialysis cannot be recommended as standard of care.
Keywords: HCO dialysis; Humans; Immunoglobulin Light Chains; Molecular Weight; Myeloma Proteins; Plasma Exchange; Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic; Standard of Care; Uromodulin; acute renal failure; cast nephropathy; free light chains; multiple myeloma; multiple myeloma M-proteins; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA: Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin 50: 7–33, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Korbet SM, Schwartz MM: Multiple myeloma. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 2533–2545, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou V, Bamias A, Gika D, Simeonidis A, Pouli A, Anagnostopoulos A, Michali E, Economopoulos T, Zervas K, Dimopoulos MA; Greek Myeloma Study Group: Renal failure in multiple myeloma: Incidence, correlations, and prognostic significance. Leuk Lymphoma 48: 337–341, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar SV, Dimopoulos MA, Palumbo A, Blade J, Merlini G, Mateos MV, Kumar S, Hillengass J, Kastritis E, Richardson P, Landgren O, Paiva B, Dispenzieri A, Weiss B, LeLeu X, Zweegman S, Lonial S, Rosinol L, Zamagni E, Jagannath S, Sezer O, Kristinsson SY, Caers J, Usmani SZ, Lahuerta JJ, Johnsen HE, Beksac M, Cavo M, Goldschmidt H, Terpos E, Kyle RA, Anderson KC, Durie BG, Miguel JF: International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol 15: e538–e548, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulos MA, Sonneveld P, Leung N, Merlini G, Ludwig H, Kastritis E, Goldschmidt H, Joshua D, Orlowski RZ, Powles R, Vesole DH, Garderet L, Einsele H, Palumbo A, Cavo M, Richardson PG, Moreau P, San Miguel J, Rajkumar SV, Durie BG, Terpos E: International Myeloma Working Group recommendations for the diagnosis and management of myeloma-related renal impairment. J Clin Oncol 34: 1544–1557, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

