Intracellular Tenofovir and Emtricitabine Anabolites in Genital, Rectal, and Blood Compartments from First Dose to Steady State
- PMID: 27526873
- PMCID: PMC5067852
- DOI: 10.1089/AID.2016.0008
Intracellular Tenofovir and Emtricitabine Anabolites in Genital, Rectal, and Blood Compartments from First Dose to Steady State
Abstract
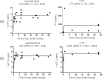
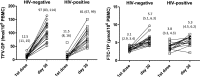
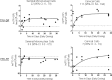
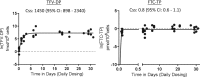
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of tenofovir-diphosphate (TFV-DP) and emtricitabine-triphosphate (FTC-TP), the active anabolites of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and emtricitabine (FTC) in blood, genital, and rectal compartments was determined in HIV-positive and seronegative adults who undertook a 60-day intensive PK study of daily TDF/FTC (plus efavirenz in HIV positives). Lymphocyte cell sorting, genital, and rectal sampling occurred once per subject, at staggered visits. Among 19 HIV-positive (3 female) and 21 seronegative (10 female) adults, TFV-DP in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) accumulated 8.6-fold [95% confidence interval (CI): 7.2-10] from first-dose to steady-state concentration (Css) versus 1.7-fold (95% CI: 1.5-1.9) for FTC-TP. Css was reached in ∼11 and 3 days, respectively. Css values were similar between HIV-negative and HIV-positive individuals. Css TFV-DP in rectal mononuclear cells (1,450 fmol/106 cells, 898-2,340) was achieved in 5 days and was >10 times higher than PBMC (95 fmol/106 cells, 85-106), seminal cells (22 fmol/106 cells, 6-79), and cervical cells (111 fmol/106 cells, 64-194). FTC-TP Css was highest in PBMC (5.7 pmol/106 cells, 5.2-6.1) and cervical cells (7 pmol/106 cells, 2-19) versus rectal (0.8 pmol/106 cells, 0.6-1.1) and seminal cells (0.3 pmol/106 cells, 0.2-0.5). Genital drug concentrations on days 1-7 overlapped with estimated Css, but accumulation characteristics were based on limited data. TFV-DP and FTC-TP in cell sorted samples were highest and achieved most rapidly in CD14+ compared with CD4+, CD8+, and CD19+ cells. Together, these findings demonstrate cell-type and tissue-dependent cellular pharmacology, preferential accumulation of TFV-DP in rectal mononuclear cells, and rapid distribution into rectal and genital compartments.
Keywords: HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis; genital compartment; intracellular; nucleoside analog; pharmacokinetics; rectal compartment.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Disclosure Statement Peter Anderson receives contract work and grant support from Gilead Sciences, paid to his institution. All other authors report no competing financial interests exit.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Model Linking Plasma and Intracellular Tenofovir/Emtricitabine with Deoxynucleoside Triphosphates.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 10;11(11):e0165505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165505. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27832147 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring potential drug-drug interactions between masculinizing hormone therapy and oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (F/TDF and F/TAF) among transgender men (iMACT study): a randomized, open-label pharmacokinetic study in Thailand.J Int AIDS Soc. 2025 Apr;28(4):e26445. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26445. J Int AIDS Soc. 2025. PMID: 40195242 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dose response for starting and stopping HIV preexposure prophylaxis for men who have sex with men.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Mar 1;60(5):804-10. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu916. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25409469 Free PMC article.
-
Emtricitabine/tenofovir in the treatment of HIV infection: current PK/PD evaluation.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012 Oct;8(10):1305-14. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2012.714367. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22943210 Review.
-
Should we fear resistance from tenofovir/emtricitabine preexposure prophylaxis?Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016 Jan;11(1):49-55. doi: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000209. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26633640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in people with HIV infection.AIDS. 2022 Dec 1;36(15):2171-2179. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003372. Epub 2022 Aug 23. AIDS. 2022. PMID: 36382436 Free PMC article.
-
Association of tenofovir diphosphate and lamivudine triphosphate concentrations with HIV and hepatitis B virus viral suppression.AIDS. 2024 Mar 1;38(3):351-362. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003764. Epub 2023 Nov 22. AIDS. 2024. PMID: 37861682 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Models to Predict Target Concentrations for Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis in Women.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2022 Dec;38(12):909-923. doi: 10.1089/AID.2022.0057. Epub 2022 Oct 25. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2022. PMID: 36097755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated rectal application of a hyperosmolar lubricant is associated with microbiota shifts but does not affect PrEP drug concentrations: results from a randomized trial in men who have sex with men.J Int AIDS Soc. 2018 Oct;21(10):e25199. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25199. J Int AIDS Soc. 2018. PMID: 30378274 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Depot Medroxyprogesterone Acetate and the Vaginal Microbiome as Modifiers of Tenofovir Diphosphate and Lamivudine Triphosphate Concentrations in the Female Genital Tract of Ugandan Women: Implications for Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate/Lamivudine in Preexposure Prophylaxis.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 10;70(8):1717-1724. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz443. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31131846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services; Available at www.aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/adultandadolescentgl.pdf accessed January1, 2016
-
- FDA: Press announcements – FDA approves first drug for reducing the risk of sexually acquired HIV infection. Available at www.fda.gov/newsevents/newsroom/pressannouncements/ucm312210.htm, accessed November25, 2014
-
- World Health Organization: Guideline on When to Start Antiretroviral Therapy and on Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available at www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/prepguidelines2014.pdf accessed December12, 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

