A self-enhanced transport mechanism through long noncoding RNAs for X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 27527711
- PMCID: PMC4985753
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31517
A self-enhanced transport mechanism through long noncoding RNAs for X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
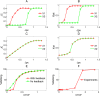
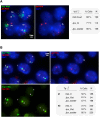
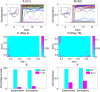
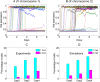
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is the mammalian dosage compensation strategy for balancing sex chromosome content between females and males. While works exist on initiation of symmetric breaking, the underlying allelic choice mechanisms and dynamic regulation responsible for the asymmetric fate determination of XCI remain elusive. Here we combine mathematical modeling and experimental data to examine the mechanism of XCI fate decision by analyzing the signaling regulatory circuit associated with long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) involved in XCI. We describe three plausible gene network models that incorporate features of lncRNAs in their localized actions and rapid transcriptional turnovers. In particular, we show experimentally that Jpx (a lncRNA) is transcribed biallelically, escapes XCI, and is asymmetrically dispersed between two X's. Subjecting Jpx to our test of model predictions against previous experimental observations, we identify that a self-enhanced transport feedback mechanism is critical to XCI fate decision. In addition, the analysis indicates that an ultrasensitive response of Jpx signal on CTCF is important in this mechanism. Overall, our combined modeling and experimental data suggest that the self-enhanced transport regulation based on allele-specific nature of lncRNAs and their temporal dynamics provides a robust and novel mechanism for bi-directional fate decisions in critical developmental processes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The trans-activator RNF12 and cis-acting elements effectuate X chromosome inactivation independent of X-pairing.Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 20;53(6):965-78. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24613346
-
Jpx RNA activates Xist by evicting CTCF.Cell. 2013 Jun 20;153(7):1537-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.028. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23791181 Free PMC article.
-
Function and evolution of the long noncoding RNA circuitry orchestrating X-chromosome inactivation in mammals.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):702-22. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1359. Epub 2016 May 13. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27173581 Review.
-
X chromosome inactivation and embryonic stem cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;695:132-54. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7037-4_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21222204
-
Guided by RNAs: X-inactivation as a model for lncRNA function.J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 9;425(19):3698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.06.031. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23816838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The metabolic role of LncZBTB39-1:2 in the trophoblast mobility of preeclampsia.Genes Dis. 2018 Apr 24;5(3):235-244. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2018.04.005. eCollection 2018 Sep. Genes Dis. 2018. PMID: 30320188 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer effects of melatonin via regulating lncRNA JPX-Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(20):9543-9556. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16894. Epub 2021 Sep 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34547170 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA Jpx induces Xist expression in mice using both trans and cis mechanisms.PLoS Genet. 2018 May 7;14(5):e1007378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007378. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29734339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Payer B. & Lee J. T. X chromosome dosage compensation: how mammals keep the balance. Annu. Rev. Genet. 42, 733–772 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Brown C. J. et al.. The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 71, 527–542 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N. et al.. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell 71, 515–526 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Penny G. D., Kay G. F., Sheardown S. a., Rastan S. & Brockdorff N. Requirement for Xist in X chromosome inactivation. Nature 379, 131–137 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Wutz A., Rasmussen T. P. & Jaenisch R. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nat. Genet. 30, 167–174 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

