Stromal remodeling by the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 suppresses the progression of human pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 27528027
- PMCID: PMC5308665
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11129
Stromal remodeling by the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 suppresses the progression of human pancreatic cancer
Abstract
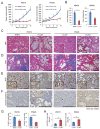
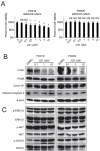
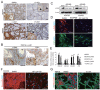
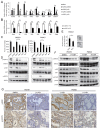
Inhibitors of bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) proteins, a family of chromatin reader proteins, have therapeutic efficacy against various malignancies. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying the anti-tumor effects in distinct tumor types remain elusive. Here, we show a novel antitumor mechanism of BET inhibition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We found that JQ1, a BET inhibitor, decreased desmoplastic stroma, a hallmark of PDAC, and suppressed the growth of patient-derived tumor xenografts (PDX) of PDACs. In vivo antitumor effects of JQ1 were not always associated with the JQ1 sensitivity of respective PDAC cells, and were rather dependent on the suppression of tumor-promoting activity in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). JQ1 inhibited Hedgehog and TGF-β pathways as potent regulators of CAF activation and suppressed the expression of α-SMA, extracellular matrix, cytokines, and growth factors in human primary CAFs. Consistently, conditioned media (CM) from CAFs promoted the proliferation of PDAC cells along with the activation of ERK, AKT, and STAT3 pathways, though these effects were suppressed when CM from JQ1-treated CAFs was used. Mechanistically, chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that JQ1 reduced TGF-β-dependent gene expression by disrupting the recruitment of the transcriptional machinery containing BET proteins. Finally, combination therapy with gemcitabine plus JQ1 showed greater efficacy than gemcitabine monotherapy against PDAC in vivo. Thus, our results reveal BET proteins as the critical regulators of CAF-activation and also provide evidence that stromal remodeling by epigenetic modulators can be a novel therapeutic option for PDAC.
Keywords: JQ1; bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) proteins; cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF); epigenetics; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The BET inhibitor JQ1 attenuates double-strand break repair and sensitizes models of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to PARP inhibitors.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jun;44:419-430. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.05.035. Epub 2019 May 22. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31126889 Free PMC article.
-
The BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 suppresses growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in patient-derived xenograft models.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 18;35(7):833-45. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.126. Epub 2015 May 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25961927 Free PMC article.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors suppress EWS-FLI1-dependent transcription and the IGF1 autocrine mechanism in Ewing sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43504-43517. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9762. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27259270 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities and delusions regarding drug delivery targeting pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 May;172:37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33705881 Review.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors--a novel epigenetic approach in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1583-5. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962297. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25535892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Stromal and Immune Cells and Therapeutic Targets in the Tumor Microenvironment.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):71. doi: 10.3390/biom15010071. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: Activation of GLI Transcription Factors Beyond Smoothened.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 12;10:556. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00556. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31244888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A peek into cancer-associated fibroblasts: origins, functions and translational impact.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Apr 19;11(4):dmm029447. doi: 10.1242/dmm.029447. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29686035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Epigenetic Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer, a New Path to Improve Patient Outcomes?Cancers (Basel). 2018 Apr 28;10(5):128. doi: 10.3390/cancers10050128. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29710783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stromal fibroblast growth factor 2 reduces the efficacy of bromodomain inhibitors in uveal melanoma.EMBO Mol Med. 2019 Feb;11(2):e9081. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809081. EMBO Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30610113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang D, Wang D, Yuan Z, Xue X, Zhang Y, An Y, Chen J, Tu M, Lu Z, Wei J, Jiang K, Miao Y. Persistent activation of pancreatic stellate cells creates a microenvironment favorable for the malignant behavior of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:993–1003. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dawson MA, Prinjha RK, Dittmann A, Giotopoulos G, Bantscheff M, Chan WI, Robson SC, Chung CW, Hopf C, Savitski MM, Huthmacher C, Gudgin E, Lugo D, et al. Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature. 2011;478:529–33. doi: 10.1038/nature10509. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

