Synthesis of structured triacylglycerols enriched in n-3 fatty acids by immobilized microbial lipase
- PMID: 27528087
- PMCID: PMC5052365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjm.2016.07.003
Synthesis of structured triacylglycerols enriched in n-3 fatty acids by immobilized microbial lipase
Abstract
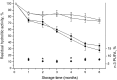
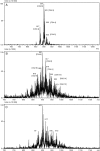
The search for new biocatalysts has aroused great interest due to the variety of micro-organisms and their role as enzyme producers. Native lipases from Aspergillus niger and Rhizopus javanicus were used to enrich the n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids content in the triacylglycerols of soybean oil by acidolysis with free fatty acids from sardine oil in solvent-free media. For the immobilization process, the best lipase/support ratios were 1:3 (w/w) for Aspergillus niger lipase and 1:5 (w/w) for Rhizopus javanicus lipase using Amberlite MB-1. Both lipases maintained constant activity for 6 months at 4°C. Reaction time, sardine-free fatty acids:soybean oil mole ratio and initial water content of the lipase were investigated to determine their effects on n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids incorporation into soybean oil. Structured triacylglycerols with 11.7 and 7.2% of eicosapentaenoic acid+docosahexaenoic acid were obtained using Aspergillus niger lipase and Rhizopus javanicus lipase, decreasing the n-6/n-3 fatty acids ratio of soybean oil (11:1 to 3.5:1 and 4.7:1, respectively). The best reaction conditions were: initial water content of lipase of 0.86% (w/w), sardine-free faty acids:soybean oil mole ratio of 3:1 and reaction time of 36h, at 40°C. The significant factors for the acidolysis reaction were the sardine-free fatty acids:soybean oil mole ratio and reaction time. The characterization of structured triacylglycerols was obtained using easy ambient sonic-spray ionization mass spectrometry. The enzymatic reaction led to the formation of many structured triacylglycerols containing eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid or both polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Keywords: Immobilization; Lipase; Polyunsaturated fatty acids; Soybean oil.
Copyright © 2016 Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A computational search for lipases that can preferentially hydrolyze long-chain omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil triacylglycerols.Food Chem. 2015 Apr 15;173:1030-6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.124. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25466121
-
Enrichment of eicosapentaenoic acid from sardine oil with Delta5-olefinic bond specific lipase from Bacillus licheniformis MTCC 6824.J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Feb 27;56(4):1428-33. doi: 10.1021/jf073176u. Epub 2008 Feb 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. PMID: 18237134
-
Lipase-catalyzed interesterification of soybean oil with an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid concentrate prepared from sardine oil.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2003 Feb;104(2):105-18. doi: 10.1385/abab:104:2:105. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12603099
-
Enzymatic modification to produce health-promoting lipids from fish oil, algae and other new omega-3 sources: A review.N Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 25;57:45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2020.02.006. Epub 2020 Mar 26. N Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32224214 Review.
-
Enzymes in Lipid Modification.Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2018 Mar 25;9:85-103. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030117-012336. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 29350562 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Structured Fatty Acids Enriched with Medium and Long-Chain n-3 Fatty Acids via Solvent-Free Transesterification of Skipjack Tuna Eyeball Oil and Commercial Butterfat.Foods. 2024 Jan 22;13(2):347. doi: 10.3390/foods13020347. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38275715 Free PMC article.
-
Structured Triacylglycerol with Optimal Arachidonic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid Content for Infant Formula Development: A Bio-Accessibility Study.Foods. 2024 Sep 2;13(17):2797. doi: 10.3390/foods13172797. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39272562 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: a comprehensive review.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Aug 26;19(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01428-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32847584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enzymatic Synthesis of Human Milk Fat Substitute - A Review on Technological Approaches.Food Technol Biotechnol. 2021 Dec;59(4):475-495. doi: 10.17113/ftb.59.04.21.7205. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 35136372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carvalho P.O., Contesini F.J., Bizaco R., Macedo G.A. Kinetic properties and enantioselectivity of the lipases produced by four Aspergillus species. Food Biotechnol. 2005;19:183–192.
-
- Contesini F.J., Lopes D.B., Macedo G.A., Nascimento M.G., Carvalho P.O. Aspergillus sp. lipase: potential biocatalyst for industrial use. J Mol Catal B: Enzym. 2010;67:163–171.
-
- Silva V.C.F., Contesini F.J., Carvalho P.O. Enantioselective behavior of lipases from Aspergillus niger immobilized in different supports. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;36:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho P.O., Campos P.R.B., Noffs M.D.A., Fregolente P.B.L., Fregolente L. Enzymatic hydrolysis of salmon oil by native lipases: optimization of process parameters. J Braz Chem Soc. 2009;20:117–124.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
