PTRF/Cavin-1 promotes efficient ribosomal RNA transcription in response to metabolic challenges
- PMID: 27528195
- PMCID: PMC4987143
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.17508
PTRF/Cavin-1 promotes efficient ribosomal RNA transcription in response to metabolic challenges
Abstract
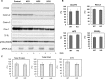
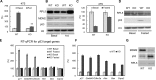
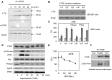
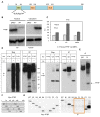
Ribosomal RNA transcription mediated by RNA polymerase I represents the rate-limiting step in ribosome biogenesis. In eukaryotic cells, nutrients and growth factors regulate ribosomal RNA transcription through various key factors coupled to cell growth. We show here in mature adipocytes, ribosomal transcription can be acutely regulated in response to metabolic challenges. This acute response is mediated by PTRF (polymerase I transcription and release factor, also known as cavin-1), which has previously been shown to play a critical role in caveolae formation. The caveolae-independent rDNA transcriptional role of PTRF not only explains the lipodystrophy phenotype observed in PTRF deficient mice and humans, but also highlights its crucial physiological role in maintaining adipocyte allostasis. Multiple post-translational modifications of PTRF provide mechanistic bases for its regulation. The role of PTRF in ribosomal transcriptional efficiency is likely relevant to many additional physiological situations of cell growth and organismal metabolism.
Keywords: adipocyte; biochemistry; cell biology; human; lipodystrophy; mouse; rat; ribosomal transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
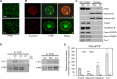
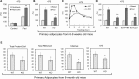

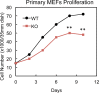
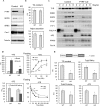
Similar articles
-
Lessons from cavin-1 deficiency.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):147-154. doi: 10.1042/BST20190380. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31922193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcript release factor PTRF augments ribosomal gene transcription by facilitating reinitiation of RNA polymerase I.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jan 15;29(2):423-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.2.423. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11139612 Free PMC article.
-
PTRF/Cavin-1 Deficiency Causes Cardiac Dysfunction Accompanied by Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy and Cardiac Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 9;11(9):e0162513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162513. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27612189 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal leucine-zipper motif in PTRF/cavin-1 is essential and sufficient for its caveolae-association.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jan 16;456(3):750-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.035. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25514038
-
Emerging role of polymerase-1 and transcript release factor (PTRF/ Cavin-1) in health and disease.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Sep;357(3):505-13. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1964-z. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 25107607 Review.
Cited by
-
Patterns of human and porcine gammaherpesvirus-encoded BILF1 receptor endocytosis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Feb 21;28(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00427-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 36810008 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal alcohol alters inflammatory signatures in enteric portal tissues following adult-onset cerebrovascular ischemic stroke.iScience. 2023 Sep 13;26(10):107920. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107920. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37810225 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoosmotic stress shifts transcription of circadian genes.Biophys J. 2025 Feb 4;124(3):565-573. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.12.027. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Biophys J. 2025. PMID: 39754358
-
Transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair is coordinated by ubiquitin and SUMO in response to ultraviolet irradiation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 10;48(1):231-248. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz977. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31722399 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from cavin-1 deficiency.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):147-154. doi: 10.1042/BST20190380. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31922193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aboulaich N, Vainonen JP, Strålfors P, Vener AV. Vectorial proteomics reveal targeting, phosphorylation and specific fragmentation of polymerase I and transcript release factor (PTRF) at the surface of caveolae in human adipocytes. Biochemical Journal. 2004;383:237–248. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040647. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bastiani M, Liu L, Hill MM, Jedrychowski MP, Nixon SJ, Lo HP, Abankwa D, Luetterforst R, Fernandez-Rojo M, Breen MR, Gygi SP, Vinten J, Walser PJ, North KN, Hancock JF, Pilch PF, Parton RG. MURC/Cavin-4 and cavin family members form tissue-specific caveolar complexes. Journal of Cell Biology. 2009;185:1259–1273. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200903053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

