Genomic and expression analyses of Tursiops truncatus T cell receptor gamma (TRG) and alpha/delta (TRA/TRD) loci reveal a similar basic public γδ repertoire in dolphin and human
- PMID: 27528257
- PMCID: PMC4986337
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2841-9
Genomic and expression analyses of Tursiops truncatus T cell receptor gamma (TRG) and alpha/delta (TRA/TRD) loci reveal a similar basic public γδ repertoire in dolphin and human
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Genomic and expression analyses of Tursiops truncatus T cell receptor gamma (TRG) and alpha/delta (TRA/TRD) loci reveal a similar basic public γδ repertoire in dolphin and human.BMC Genomics. 2016 Oct 5;17(1):778. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3142-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27716050 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) is a mammal that belongs to the Cetartiodactyla and have lived in marine ecosystems for nearly 60 millions years. Despite its popularity, our knowledge about its adaptive immunity and evolution is very limited. Furthermore, nothing is known about the genomics and evolution of dolphin antigen receptor immunity.
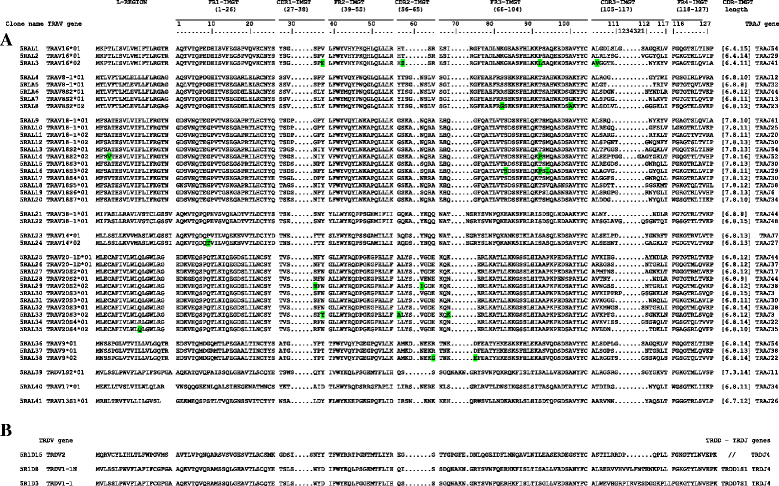
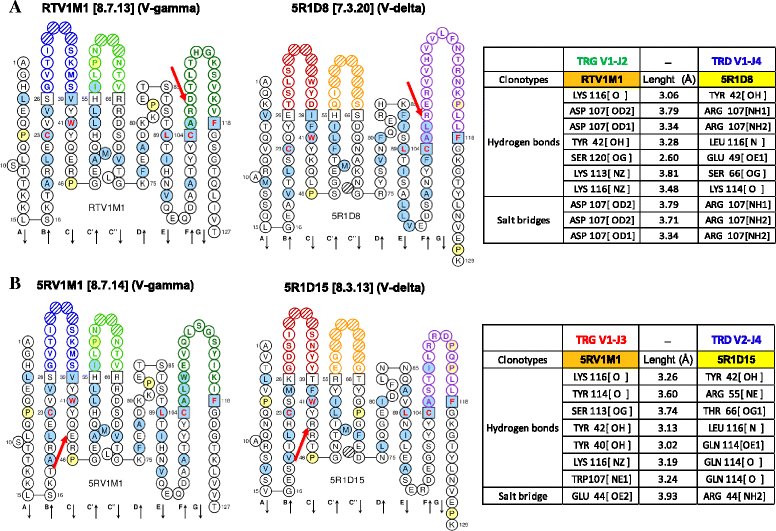
Results: Here we report a evolutionary and expression study of Tursiops truncatus T cell receptor gamma (TRG) and alpha/delta (TRA/TRD) genes. We have identified in silico the TRG and TRA/TRD genes and analyzed the relevant mature transcripts in blood and in skin from four subjects. The dolphin TRG locus is the smallest and simplest of all mammalian loci as yet studied. It shows a genomic organization comprising two variable (V1 and V2), three joining (J1, J2 and J3) and a single constant (C), genes. Despite the fragmented nature of the genome assemblies, we deduced the TRA/TRD locus organization, with the recent TRDV1 subgroup genes duplications, as it is expected in artiodactyls. Expression analysis from blood of a subject allowed us to assign unambiguously eight TRAV genes to those annotated in the genomic sequence and to twelve new genes, belonging to five different subgroups. All transcripts were productive and no relevant biases towards TRAV-J rearrangements are observed. Blood and skin from four unrelated subjects expression data provide evidence for an unusual ratio of productive/unproductive transcripts which arise from the TRG V-J gene rearrangement and for a "public" gamma delta TR repertoire. The productive cDNA sequences, shared both in the same and in different individuals, include biases of the TRGV1 and TRGJ2 genes. The high frequency of TRGV1-J2/TRDV1- D1-J4 productive rearrangements in dolphins may represent an interesting oligo-clonal population comparable to that found in human with the TRGV9- JP/TRDV2-D-J T cells and in primates.
Conclusions: Although the features of the TRG and TRA/TRD loci organization reflect those of the so far examined artiodactyls, genomic results highlight in dolphin an unusually simple TRG locus. The cDNA analysis reveal productive TRA/TRD transcripts and unusual ratios of productive/unproductive TRG transcripts. Comparing multiple different individuals, evidence is found for a "public" gamma delta TCR repertoire thus suggesting that in dolphins as in human the gamma delta TCR repertoire is accompanied by selection for public gamma chain.
Keywords: Dolphin genome; Expression analysis; IMGT; T cell receptor; TRA/TRD locus; TRAV and TRDV genes; TRG locus; TRGJ and TRGC genes; TRGV.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

