Xist and Tsix Transcription Dynamics Is Regulated by the X-to-Autosome Ratio and Semistable Transcriptional States
- PMID: 27528619
- PMCID: PMC5064214
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00183-16
Xist and Tsix Transcription Dynamics Is Regulated by the X-to-Autosome Ratio and Semistable Transcriptional States
Abstract
In female mammals, X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a key process in the control of gene dosage compensation between X-linked genes and autosomes. Xist and Tsix, two overlapping antisense-transcribed noncoding genes, are central elements of the X inactivation center (Xic) regulating XCI. Xist upregulation results in the coating of the entire X chromosome by Xist RNA in cis, whereas Tsix transcription acts as a negative regulator of Xist Here, we generated Xist and Tsix reporter mouse embryonic stem (ES) cell lines to study the genetic and dynamic regulation of these genes upon differentiation. Our results revealed mutually antagonistic roles for Tsix on Xist and vice versa and indicate the presence of semistable transcriptional states of the Xic locus predicting the outcome of XCI. These transcriptional states are instructed by the X-to-autosome ratio, directed by regulators of XCI, and can be modulated by tissue culture conditions.
Copyright © 2016 Loos et al.
Figures
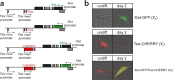
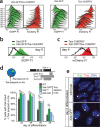
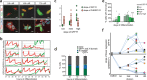

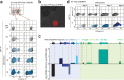

Similar articles
-
Loss of One X and the Y Chromosome Changes the Configuration of the X Inactivation Center in the Genus Tokudaia.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2024;164(1):23-32. doi: 10.1159/000539294. Epub 2024 May 16. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 38754392
-
The Ftx Noncoding Locus Controls X Chromosome Inactivation Independently of Its RNA Products.Mol Cell. 2018 May 3;70(3):462-472.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.03.024. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29706539
-
Tsix transcription across the Xist gene alters chromatin conformation without affecting Xist transcription: implications for X-chromosome inactivation.Genes Dev. 2005 Jun 15;19(12):1474-84. doi: 10.1101/gad.341105. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15964997 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interplay and function of multiple noncoding genes governing X chromosome inactivation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1859(1):112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26260844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What makes the maternal X chromosome resistant to undergoing imprinted X inactivation?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20160365. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0365. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947661 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations in expression of miRNA 497 and long non-coding RNAS (XIST-TSIX) and its significant role in colorectal cancer prediction.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 3;15(1):7387. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90110-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40032945 Free PMC article.
-
A symmetric toggle switch explains the onset of random X inactivation in different mammals.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 May;26(5):350-360. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0214-1. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30962582 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular and Nuclear Dynamics of X-Chromosome Inactivation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022 May 17;14(4):a040196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022. PMID: 34312245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchestrating Asymmetric Expression: Mechanisms behind Xist Regulation.Epigenomes. 2024 Feb 1;8(1):6. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8010006. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 38390897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Conserved Noncoding Locus Regulates Random Monoallelic Xist Expression across a Topological Boundary.Mol Cell. 2020 Jan 16;77(2):352-367.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.030. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31759823 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
