Genome-wide quantification of rare somatic mutations in normal human tissues using massively parallel sequencing
- PMID: 27528664
- PMCID: PMC5024639
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1607794113
Genome-wide quantification of rare somatic mutations in normal human tissues using massively parallel sequencing
Abstract
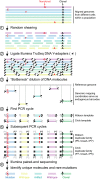
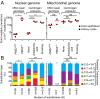
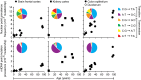
We present the bottleneck sequencing system (BotSeqS), a next-generation sequencing method that simultaneously quantifies rare somatic point mutations across the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes. BotSeqS combines molecular barcoding with a simple dilution step immediately before library amplification. We use BotSeqS to show age- and tissue-dependent accumulations of rare mutations and demonstrate that somatic mutational burden in normal human tissues can vary by several orders of magnitude, depending on biologic and environmental factors. We further show major differences between the mutational patterns of the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes in normal tissues. Lastly, the mutation spectra of normal tissues were different from each other, but similar to those of the cancers that arose in them. This technology can provide insights into the number and nature of genetic alterations in normal tissues and can be used to address a variety of fundamental questions about the genomes of diseased tissues.
Keywords: aging; genomics; next-generation sequencing; somatic mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
B.V. has no conflict of interest with respect to the new technology described in this manuscript, as defined by Johns Hopkins University's policy on conflict of interest. B.V. is a founder of PapGene and Personal Genome Diagnostics and a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of Morphotek and Syxmex-Inostics. These companies and others have licensed patent applications on genetic technologies from Johns Hopkins, some of which result in royalty payments to B.V. The terms of these arrangements are being managed by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures
References
-
- Albertini RJ, Nicklas JA, O’Neill JP, Robison SH. In vivo somatic mutations in humans: Measurement and analysis. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:305–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

