Primary spinal cord epidural non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma as cause of paraplegia: report of 2 cases
- PMID: 27528963
- PMCID: PMC3345441
- DOI: 10.4314/mmj.v15i2.10782
Primary spinal cord epidural non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma as cause of paraplegia: report of 2 cases
Abstract
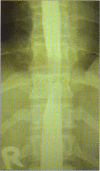
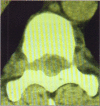
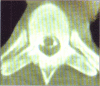
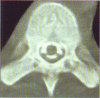
Two cases of paraplegia due to primary spinal cord epidural non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) are presented. This is a rare cause of paraplegia. The clinical presentation, investigations and management of this rare condition are outlined. A review of the literature is presented. Primary spinal epidural NHL should be considered in patients who give a history of back pain; followed by rapid development of features of spinal cord compression; have normal plain x-rays but whose CAT / myelogram reveal an extradural mass. Urgent surgical decompression followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy improves the outcome of such patients. Primary epidural Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) with no evidence of parenchymal central nervous system (CNS) or systemic involvement is rare. Although it may present as a localised disease it is in fact a systemic disease. This disease entity must be differentiated from the more common clinical situation of primary CNS parenchymal lymphoma with meningeal involvement or systemic lymphoma, such as adult cell T lymphoma, complicated by lymphomatous meningitis. A 20-year experience with NHL at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Centre showed that primary epidural NHL accounted for 2 out of 256 (1.9%) of NHL cases1. A 10-year experience (1979-1989) at the Mayo Clinic report primary spinal epidural NHL accounting for 6.6% of all cases of intraspinal NHL2. Levitt et al report that among 592 cases of NHL seen between 1967 and 1977, 52 patients (11%) had CNS lymphomatous involvement. However they did not specify how many were primary spinal epidural NHL3. With the current AIDS/HIV pan epidemic it is expected that the incidence of primary spinal NHL will increase. Distinguishing primary spinal NHL from an infectious spinal mass may be difficult as both would present with similar features of meningitis, fever, night sweats and weight loss.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CNS involvement in the non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.Cancer. 1980 Feb;45(3):545-52. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800201)45:3<545::aid-cncr2820450322>3.0.co;2-6. Cancer. 1980. PMID: 6986199
-
Primary epidural non-Hodgkin lymphoma: spinal cord compression syndrome as the initial form of presentation in childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Med Pediatr Oncol. 1999 Feb;32(2):102-5. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-911x(199902)32:2<102::aid-mpo6>3.0.co;2-y. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1999. PMID: 9950197
-
Primary spinal epidural non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: report of eight patients and review of the literature.Neurosurgery. 1992 May;30(5):675-80. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199205000-00004. Neurosurgery. 1992. PMID: 1584377 Review.
-
Primary Lumbo-sacral Spinal Epidural Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Asian Spine J. 2011 Sep;5(3):192-5. doi: 10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.192. Epub 2011 Aug 12. Asian Spine J. 2011. PMID: 21892393 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal epidural non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: case reports of three patients presenting with spinal cord compression.Singapore Med J. 1996 Oct;37(5):497-500. Singapore Med J. 1996. PMID: 9046202 Review.
References
-
- Mora J, Wollner N. Primary epidural non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: spinal cord compression syndrome as the initial form of presentation in childhood non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1999 Feb;32(2):102–105. - PubMed
-
- Lyons MK, O'Neill BP, Marsh WR, Kurtin PJ. Primary spinal epidural non - Hodgkin's lymphoma: report of eight patients and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1992 May;30(5):675–680. - PubMed
-
- Levitt LJ, Dawson DM, Rosenthal DS, Moloney WC. CNS involvement in the non - Hodgkin's lymphomas. Cancer. 1980 Feb;45(3):545–552. - PubMed
-
- Young RC, Howser DM, Anderson T, et al. Central nervous system complications of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The potential role for prophylactic therapy. Am J Med. 1979 Mar;66(3):435–443. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain MC, Kormanik PA. AIDS - related central nervous system lymphomas. J Neurooncol. 1999 Jul;43(3):269–276. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
