Make it SIMPLE: enhanced shock management by focused cardiac ultrasound
- PMID: 27529027
- PMCID: PMC4983798
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-016-0176-x
Make it SIMPLE: enhanced shock management by focused cardiac ultrasound
Abstract
Background: Shock is a spectrum of circulatory failure that, if not properly managed, would lead to high mortality. Special diagnostic and treatment strategies are essential to save lives. However, clinical and laboratory findings are always non-specific, resulting in clinical dilemmas.
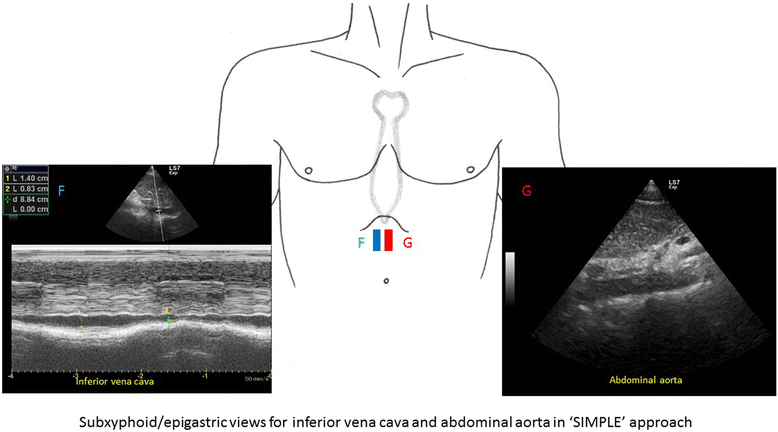
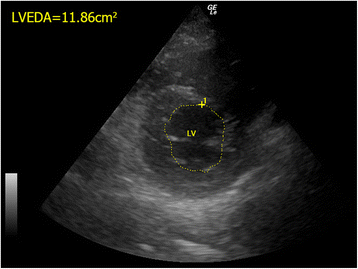
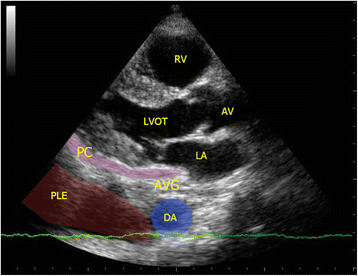
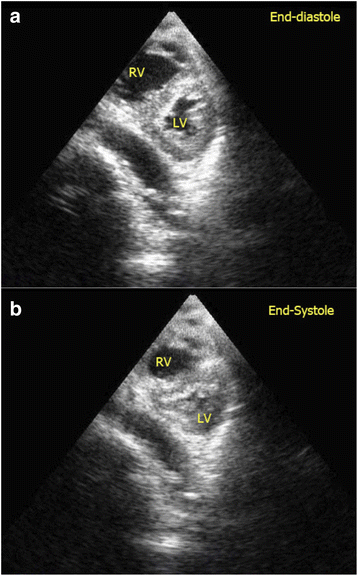
Main content: Focused cardiac ultrasound (FoCUS) has emerged as one of the power tools for clinicians to answer simple clinical questions and guide subsequent management in hypotensive patients. This article will review the development and utility of FoCUS in different types of shock. The sonographic features and ultrasound enhanced management of hypotensive patients by a de novo "SIMPLE" approach will be described. Current evidence on FoCUS will also be reviewed.
Conclusion: Focused cardiac ultrasound provides timely and valuable information for the evaluation of shock. It helps to improve the diagnostic accuracy, narrow the possible differential diagnoses, and guide specific management. SIMPLE is an easy-to-remember mnemonic for non-cardiologists or novice clinical sonographers to apply FoCUS and interpret the specific sonographic findings when evaluating patients in shock.
Keywords: Critical care; Echocardiography; Emergency department; Sepsis; Shock; Ultrasound.
Figures











References
-
- Jones AE, Kline JE: S. In: Rosen’s emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice. Volume 1. 8. Marx JA, Hockberger RS, Walls RM, editors. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2014. pp. 67–71.
-
- Holler JG, Bech CN, Henriksen DP, Mikkelsen S, Pedersen C, Lassen AT. Nontraumatic hypotension and shock in the emergency department and the prehospital setting, prevalence, etiology, and mortality: a systematic review. Calvert J, ed. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119331. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

