Genetic and Environmental Risk for Chronic Pain and the Contribution of Risk Variants for Major Depressive Disorder: A Family-Based Mixed-Model Analysis
- PMID: 27529168
- PMCID: PMC4987025
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002090
Genetic and Environmental Risk for Chronic Pain and the Contribution of Risk Variants for Major Depressive Disorder: A Family-Based Mixed-Model Analysis
Abstract
Background: Chronic pain is highly prevalent and a significant source of disability, yet its genetic and environmental risk factors are poorly understood. Its relationship with major depressive disorder (MDD) is of particular importance. We sought to test the contribution of genetic factors and shared and unique environment to risk of chronic pain and its correlation with MDD in Generation Scotland: Scottish Family Health Study (GS:SFHS). We then sought to replicate any significant findings in the United Kingdom Biobank study.
Methods and findings: Using family-based mixed-model analyses, we examined the contribution of genetics and shared family environment to chronic pain by spouse, sibling, and household relationships. These analyses were conducted in GS:SFHS (n = 23,960), a family- and population-based study of individuals recruited from the Scottish population through their general practitioners. We then examined and partitioned the correlation between chronic pain and MDD and estimated the contribution of genetic factors and shared environment in GS:SFHS. Finally, we used data from two independent genome-wide association studies to test whether chronic pain has a polygenic architecture and examine whether genomic risk of psychiatric disorder predicted chronic pain and whether genomic risk of chronic pain predicted MDD. These analyses were conducted in GS:SFHS and repeated in UK Biobank, a study of 500,000 from the UK population, of whom 112,151 had genotyping and phenotypic data. Chronic pain is a moderately heritable trait (heritability = 38.4%, 95% CI 33.6% to 43.9%) that is significantly concordant in spouses (variance explained 18.7%, 95% CI 9.5% to 25.1%). Chronic pain is positively correlated with depression (ρ = 0.13, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.15, p = 2.72x10-68) and shows a tendency to cluster within families for genetic reasons (genetic correlation = 0.51, 95%CI 0.40 to 0.62, p = 8.24x10-19). Polygenic risk profiles for pain, generated using independent GWAS data, were associated with chronic pain in both GS:SFHS (maximum β = 6.18x10-2, 95% CI 2.84 x10-2 to 9.35 x10-2, p = 4.3x10-4) and UK Biobank (maximum β = 5.68 x 10-2, 95% CI 4.70x10-2 to 6.65x10-2, p < 3x10-4). Genomic risk of MDD is also significantly associated with chronic pain in both GS:SFHS (maximum β = 6.62x10-2, 95% CI 2.82 x10-2 to 9.76 x10-2, p = 4.3x10-4) and UK Biobank (maximum β = 2.56x10-2, 95% CI 1.62x10-2 to 3.63x10-2, p < 3x10-4). Limitations of the current study include the possibility that spouse effects may be due to assortative mating and the relatively small polygenic risk score effect sizes.
Conclusions: Genetic factors, as well as chronic pain in a partner or spouse, contribute substantially to the risk of chronic pain for an individual. Chronic pain is genetically correlated with MDD, has a polygenic architecture, and is associated with polygenic risk of MDD.
Conflict of interest statement
AMM has received research funding from Pfizer, Janssen and Lilly in connection with other research. This funding had no role in the research presented in the current manuscript. DAH has received research funding from Pfizer for the current study. DAH is an employee of and owns stock options in 23andMe, Inc. WM has received research funding from Pfizer. BHS has received research funding from Pfizer and Napp Pharmaceuticals. LJH has received research funding from Pfizer. CHay has received research funding from Pfizer.
Figures
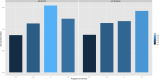
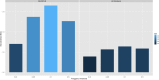
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743–800. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

