Resveratrol Attenuates Acute Inflammatory Injury in Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats via Inhibition of TLR4 Pathway
- PMID: 27529233
- PMCID: PMC5000728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17081331
Resveratrol Attenuates Acute Inflammatory Injury in Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats via Inhibition of TLR4 Pathway
Abstract
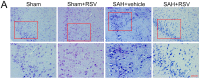
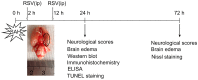
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has been proven to play a critical role in neuroinflammation and to represent an important therapeutic target following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Resveratrol (RSV), a natural occurring polyphenolic compound, has a powerful anti-inflammatory property. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms of RSV in protecting against early brain injury (EBI) after SAH remain obscure. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of RSV on the TLR4-related inflammatory signaling pathway and EBI in rats after SAH. A prechiasmatic cistern SAH model was used in our experiment. The expressions of TLR4, high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were evaluated by Western blot and immunohistochemistry. The expressions of Iba-1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines in brain cortex were determined by Western blot, immunofluorescence staining, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Neural apoptosis, brain edema, and neurological function were further evaluated to investigate the development of EBI. We found that post-SAH treatment with RSV could markedly inhibit the expressions of TLR4, HMGB1, MyD88, and NF-κB. Meanwhile, RSV significantly reduced microglia activation, as well as inflammatory cytokines leading to the amelioration of neural apoptosis, brain edema, and neurological behavior impairment at 24 h after SAH. However, RSV treatment failed to alleviate brain edema and neurological deficits at 72 h after SAH. These results indicated that RSV treatment could alleviate EBI after SAH, at least in part, via inhibition of TLR4-mediated inflammatory signaling pathway.
Keywords: early brain injury; inflammation; resveratrol; subarachnoid hemorrhage; toll-like receptor 4.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Baincalein alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: possible involvement of TLR4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway.Brain Res. 2015 Jan 12;1594:245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.10.014. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25451085
-
Pentoxifylline Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats: Possibly via Inhibiting TLR 4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2017 Apr;42(4):963-974. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2129-0. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27933551
-
Melatonin alleviates secondary brain damage and neurobehavioral dysfunction after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: possible involvement of TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway.J Pineal Res. 2013 Nov;55(4):399-408. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12087. Epub 2013 Sep 6. J Pineal Res. 2013. PMID: 24007200
-
Toll-like receptor-4 pathway as a possible molecular mechanism for brain injuries after subarachnoid hemorrhage.Int J Neurosci. 2020 Sep;130(9):953-964. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2019.1709845. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Int J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31903827 Review.
-
Signaling Pathway in Early Brain Injury after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: News Update.Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2016;121:123-6. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18497-5_21. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2016. PMID: 26463934 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Gut Microbiome with Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: an Experimental Study.Transl Stroke Res. 2024 Feb;15(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01112-6. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Transl Stroke Res. 2024. PMID: 36484924
-
Potential regulatory effects of stem cell exosomes on inflammatory response in ischemic stroke treatment.World J Stem Cells. 2023 Jun 26;15(6):561-575. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i6.561. World J Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37424949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Attenuates Early Brain Injury after Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Front Neurosci. 2017 Nov 3;11:611. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00611. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29163015 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Melatonin: Potential Functions in Improving Cerebral Autoregulation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Front Physiol. 2018 Aug 17;9:1146. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01146. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30174621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the novel biomarker and therapeutic potentials of High-mobility group box 1 in Subarachnoid hemorrhage: A review.AIMS Neurosci. 2019 Dec 2;6(4):316-332. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2019.4.316. eCollection 2019. AIMS Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 32341986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang Y., Gao A., Xu X., Dang B., You W., Li H., Yu Z., Chen G. The neuroprotection of lysosomotropic agents in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage probably involving the apoptosis pathway triggering by cathepsins via chelating intralysosomal iron. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015;52:64–77. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8846-y. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

