Skeletal Muscle Laminopathies: A Review of Clinical and Molecular Features
- PMID: 27529282
- PMCID: PMC5040975
- DOI: 10.3390/cells5030033
Skeletal Muscle Laminopathies: A Review of Clinical and Molecular Features
Abstract
LMNA-related disorders are caused by mutations in the LMNA gene, which encodes for the nuclear envelope proteins, lamin A and C, via alternative splicing. Laminopathies are associated with a wide range of disease phenotypes, including neuromuscular, cardiac, metabolic disorders and premature aging syndromes. The most frequent diseases associated with mutations in the LMNA gene are characterized by skeletal and cardiac muscle involvement. This review will focus on genetics and clinical features of laminopathies affecting primarily skeletal muscle. Although only symptomatic treatment is available for these patients, many achievements have been made in clarifying the pathogenesis and improving the management of these diseases.
Keywords: Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; LMNA gene; arrhythmia; cardiomyopathy; congenital muscular dystrophy; laminopathies; limb-girdle muscular dystrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

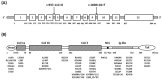
Similar articles
-
Lamin-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy Alters Mechanical Signaling and Skeletal Muscle Growth.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 30;22(1):306. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010306. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33396724 Free PMC article.
-
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, laminopathies, and other nuclear envelopathies.Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;113:1367-76. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-59565-2.00007-1. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23622360 Review.
-
Cardiac manifestations of congenital LMNA-related muscular dystrophy in children: three case reports and recommendations for care.Cardiol Young. 2017 Aug;27(6):1076-1082. doi: 10.1017/S1047951116002079. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Cardiol Young. 2017. PMID: 27938454
-
Muscle imaging analogies in a cohort of patients with different clinical phenotypes caused by LMNA gene mutations.Muscle Nerve. 2010 Apr;41(4):458-63. doi: 10.1002/mus.21514. Muscle Nerve. 2010. PMID: 19882644
-
Laminopathies affecting skeletal and cardiac muscles: clinical and pathophysiological aspects.Acta Myol. 2005 Oct;24(2):104-9. Acta Myol. 2005. PMID: 16550926 Review.
Cited by
-
Global transcriptional changes caused by an EDMD mutation correlate to tissue specific disease phenotypes in C. elegans.Nucleus. 2017 Jan 2;8(1):60-69. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1238999. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Nucleus. 2017. PMID: 27673727 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of LAP2α inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by activating NF-κB.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Jul 1;11(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01774-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32611381 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of COMMD1 as a novel lamin A binding partner.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1790-1796. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10419. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31257505 Free PMC article.
-
Defining and identifying satellite cell-opathies within muscular dystrophies and myopathies.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Feb 1;411(1):112906. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112906. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 34740639 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-phenotype correlation of LMNA variants involving the Arg541 residue: a case report with multimodality imaging and literature review.ESC Heart Fail. 2020 Oct;7(5):3169-3173. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12776. Epub 2020 Jul 15. ESC Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 32667740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonne G., Yaou R.B., Béroud C., Boriani G., Brown S., de Visser M., Duboc D., Ellis J., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Lattanzi G., et al. 108th ENMC International Workshop, 3rd Workshop of the MYO-CLUSTER project: EUROMEN, 7th International Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) Workshop, 13–15 September 2002, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2003;13:508–515. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8966(03)00063-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

