Systematic Review of Micro-RNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia Identifies a Number of Common Pathways Associated with the Disease
- PMID: 27529341
- PMCID: PMC4986940
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160808
Systematic Review of Micro-RNA Expression in Pre-Eclampsia Identifies a Number of Common Pathways Associated with the Disease
Abstract
Background: Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a complex, multi-systemic condition of pregnancy which greatly impacts maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. MicroRNAs (miRs) are differentially expressed in PE and may be important in helping to understand the condition and its pathogenesis.
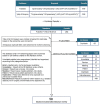
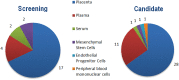
Methods: Case-control studies investigating expression of miRs in PE were collected through a systematic literature search. Data was extracted and compared from 58 studies to identify the most promising miRs associated with PE pathogenesis and identify areas of methodology which could account for often conflicting results.
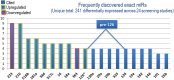
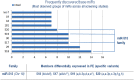
Results: Some of the most frequently differentially expressed miRs in PE include miR-210, miR-223 and miR-126/126* which associate strongly with the etiological domains of hypoxia, immunology and angiogenesis. Members of the miR-515 family belonging to the imprinted chromosome 19 miR cluster with putative roles in trophoblast invasion were also found to be differentially expressed. Certain miRs appear to associate with more severe forms of PE such as miR-210 and the immune-related miR-181a and miR-15 families. Patterns of miR expression may help pinpoint key pathways (e.g. IL-6/miR-223/STAT3) and aid in untangling the heterogeneous nature of PE. The detectable presence of many PE-associated miRs in antenatal circulatory samples suggests their usefulness as predictive biomarkers. Further progress in ascertaining the clinical value of miRs and in understanding how they might contribute to pathogenesis is predicated upon resolving current methodological challenges in studies. These include differences in diagnostic criteria, cohort characteristics, sampling technique, RNA isolation and platform-dependent variation in miR profiling.
Conclusion: Reviewing studies of PE-associated miRs has revealed their potential as informants of underlying target genes and pathways relating to PE pathogenesis. However, the incongruity in results across current studies hampers their capacity to be useful biomarkers of the condition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deciphering Shared Gene Signatures and Immune Infiltration Characteristics Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning.Reprod Sci. 2025 Jun;32(6):1886-1904. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01847-1. Epub 2025 May 15. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40374866
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Epidural therapy for the treatment of severe pre-eclampsia in non labouring women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):CD009540. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009540.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29181841 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Sep;111(4):322-37. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw174. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27357636 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An Analysis of Mechanisms for Cellular Uptake of miRNAs to Enhance Drug Delivery and Efficacy in Cancer Chemoresistance.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Apr 16;7(2):27. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7020027. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 33923485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of MicroRNAs, Long Non-coding RNAs, and Circular RNAs in Preeclampsia.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 30;12:659638. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.659638. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33995125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Plasma miRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Moderate-to-Late-Preterm Birth.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 2;25(17):9536. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179536. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273483 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Epigenetic and Molecular Factors in Endometrium of Females with Infertility.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 4;10(6):1324. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061324. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740346 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based trends and risk factors of early- and late-onset preeclampsia in Taiwan 2001-2014.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018 May 31;18(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-1845-7. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018. PMID: 29855344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NICE. Hypertension in pregnancy: diagnosis and management. In: Hypertension in pregnancy: diagnosis and management [Internet]. [cited 28 Feb 2016]. Available: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG107/chapter/introduction
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

