Hypertonic Saline Primes Activation of the p53-p21 Signaling Axis in Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells That Prevents Inflammation Induced by Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 27529569
- PMCID: PMC5811188
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00602
Hypertonic Saline Primes Activation of the p53-p21 Signaling Axis in Human Small Airway Epithelial Cells That Prevents Inflammation Induced by Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
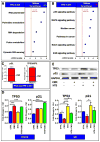
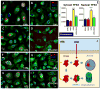
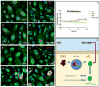
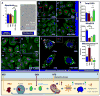
Uncontrolled inflammatory responses underlie the etiology of acute lung injury and acute distress respiratory syndrome, the most common late complications in trauma, the leading cause of death under the age of 59. Treatment with HTS decreases lung injury in clinical trials, rat models of trauma and hemorrhagic shock and inflammation in lung cell lines, although the mechanisms underlying these responses are still incompletely understood. Transcriptomics (RNaseq), proteomics, and U-13C-glucose tracing metabolomics experiments were performed to investigate the mechanisms of cellular responses to HTS treatment in primary small airway epithelial cells in the presence or absence of inflammatory injury mediated by a cocktail of cytokines (10 ng/mL of IFNγ, IL-1β, and TNFα). Modestly hyperosmolar HTS has an anti-inflammatory effect, triggers the p53-p21 signaling axis, and deregulates mitochondrial metabolism while inducing minimal apoptosis in response to a second hit by cytokines. Decreased transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines suggested a role for the tumor suppressor protein p53 in mediating the beneficial effects of the HTS treatment. The anti-inflammatory mechanisms induced by HTS involves p53 gene regulation, promotes cell cycle arrest, and prevents ROS formation and mitochondria depolarization. Pharmaceutical targeting of the p53-p21 axis may mimic or reinforce the beneficial effects mediated by HTS when sustained hypertonicity cannot be maintained.
Keywords: RNaseq; metabolomics; mitochondria; osmotic stress; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypertonic saline attenuates the cytokine-induced pro-inflammatory signature in primary human lung epithelia.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 18;12(12):e0189536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189536. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29253007 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation between p21 and Akt is required for p53-dependent cellular senescence.Aging Cell. 2017 Oct;16(5):1094-1103. doi: 10.1111/acel.12639. Epub 2017 Jul 9. Aging Cell. 2017. PMID: 28691365 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor induces cell apoptosis and cycle arrest in lung cancer cells via mitochondrial injury and p53 up-acetylation.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016 Dec;32(6):469-482. doi: 10.1007/s10565-016-9347-8. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27423454 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Wild-Type p53 Signaling in Suppressing Apoptosis in Response to Chemical Genotoxic Agents: Impact on Chemotherapy Outcome.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 28;18(5):928. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050928. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28452953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P53 versus inflammation: an update.Cell Cycle. 2020 Jan;19(2):160-162. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1708575. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 31880200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine-Ion Channel Interactions in Pulmonary Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2018 Jan 4;8:1644. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01644. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29354115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypertonic saline attenuates the cytokine-induced pro-inflammatory signature in primary human lung epithelia.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 18;12(12):e0189536. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189536. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29253007 Free PMC article.
-
Hypotheses about sub-optimal hydration in the weeks before coronavirus disease (COVID-19) as a risk factor for dying from COVID-19.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Nov;144:110237. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110237. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 33254543 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment effect of CDKN1A on rheumatoid arthritis by mediating proliferation and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes cells.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Nov;194(2):220-230. doi: 10.1111/cei.13161. Epub 2018 Sep 23. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29920650 Free PMC article.
-
Osmolar Modulation Drives Reversible Cell Cycle Exit and Human Pluripotent Cell Differentiation via NF-κВ and WNT Signaling.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Feb;11(7):e2307554. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307554. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38037844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhee P, Joseph B, Pandit V, Aziz H, Vercruysse G, Kulvatunyou N, Friese RS. Increasing trauma deaths in the United States. Ann Surg. 2014;260(1):13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

