Solid-in-oil nanodispersions for transdermal drug delivery systems
- PMID: 27529824
- PMCID: PMC5132072
- DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600081
Solid-in-oil nanodispersions for transdermal drug delivery systems
Abstract
Transdermal administration of drugs has advantages over conventional oral administration or administration using injection equipment. The route of administration reduces the opportunity for drug evacuation before systemic circulation, and enables long-lasting drug administration at a modest body concentration. In addition, the skin is an attractive route for vaccination, because there are many immune cells in the skin. Recently, solid-in-oil nanodisperison (S/O) technique has demonstrated to deliver cosmetic and pharmaceutical bioactives efficiently through the skin. S/O nanodispersions are nanosized drug carriers designed to overcome the skin barrier. This review discusses the rationale for preparation of efficient and stable S/O nanodispersions, as well as application examples in cosmetic and pharmaceutical materials including vaccines. Drug administration using a patch is user-friendly, and may improve patient compliance. The technique is a potent transcutaneous immunization method without needles.
Keywords: Nanocarrier; Solid-in-oil nanodispersion; Transcutaneous immunotherapy; Transdermal drug delivery; Vaccine.
© 2016 The Authors. Biotechnology Journal published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
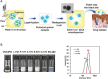
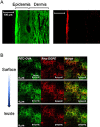
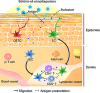
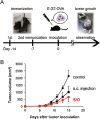
References
-
- Barry, B. W. , Novel mechanisms and devices to enable successful transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 101–114. - PubMed
-
- Thomas, B. J. , Finnin, B. C. , The transdermal revolution. Drug Discovery Today 2004, 9, 697–703. - PubMed
-
- Mitragotri, S. , Immunization without needles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 905–916. - PubMed
-
- Ita, K. B. , Transdermal drug delivery: Progress and challenges. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 245–250.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

