A combination of silver nanoparticles and visible blue light enhances the antibacterial efficacy of ineffective antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- PMID: 27530257
- PMCID: PMC4988001
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-016-0164-y
A combination of silver nanoparticles and visible blue light enhances the antibacterial efficacy of ineffective antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Abstract
Background: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are potential antimicrobials agents, which can be considered as an alternative to antibiotics for the treatment of infections caused by multi-drug resistant bacteria. The antimicrobial effects of double and triple combinations of AgNPs, visible blue light, and the conventional antibiotics amoxicillin, azithromycin, clarithromycin, linezolid, and vancomycin, against ten clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were investigated.
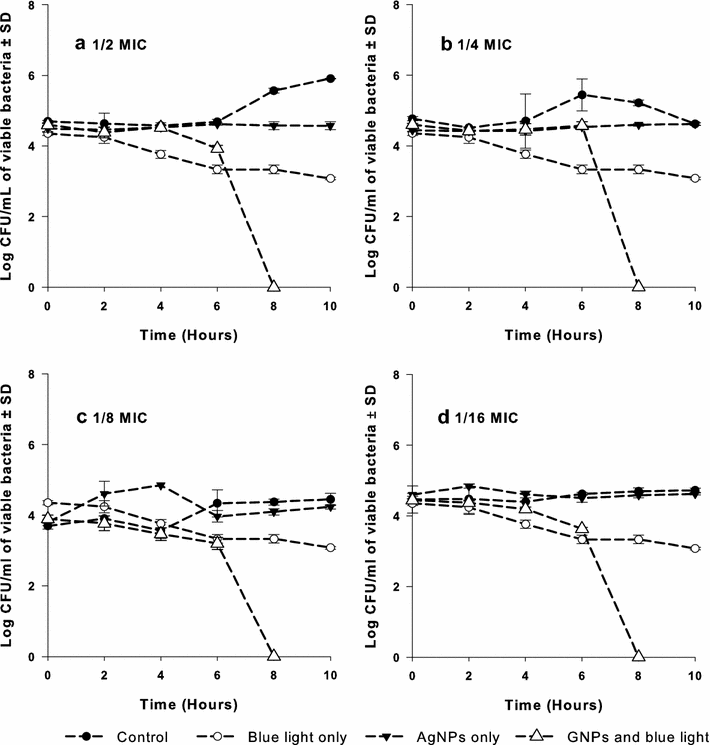
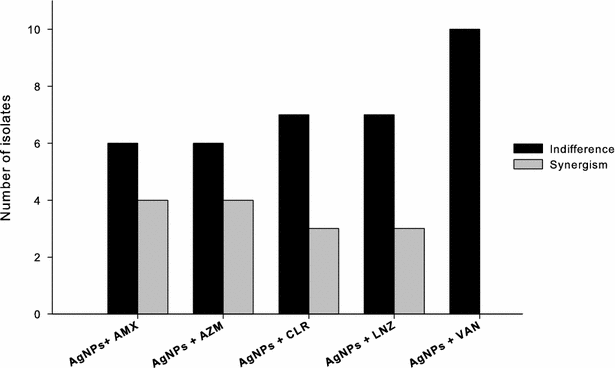
Methods: The antimicrobial activity of AgNPs, applied in combination with blue light, against selected isolates of MRSA was investigated at 1/2-1/128 of its minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) in 24-well plates. The wells were exposed to blue light source at 460 nm and 250 mW for 1 h using a photon emitting diode. Samples were taken at different time intervals, and viable bacterial counts were determined. The double combinations of AgNPs and each of the antibiotics were assessed by the checkerboard method. The killing assay was used to test possible synergistic effects when blue light was further combined to AgNPs and each antibiotic at a time against selected isolates of MRSA.
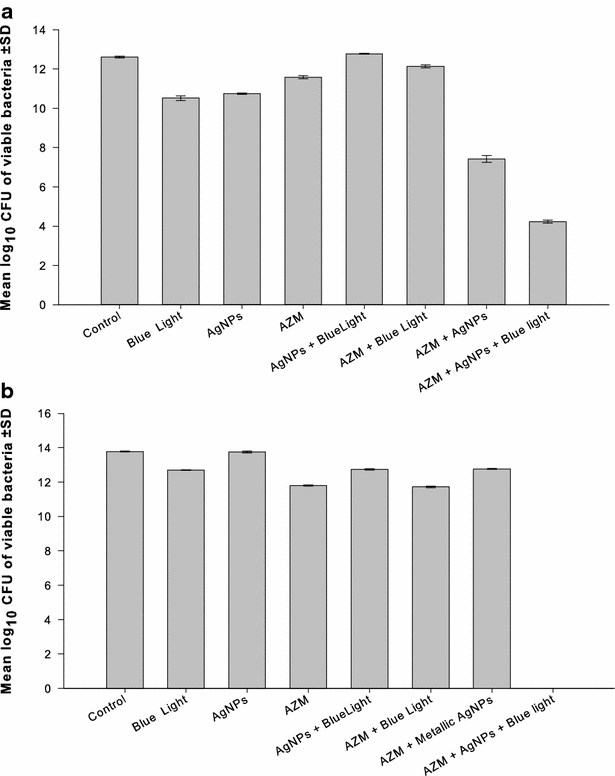
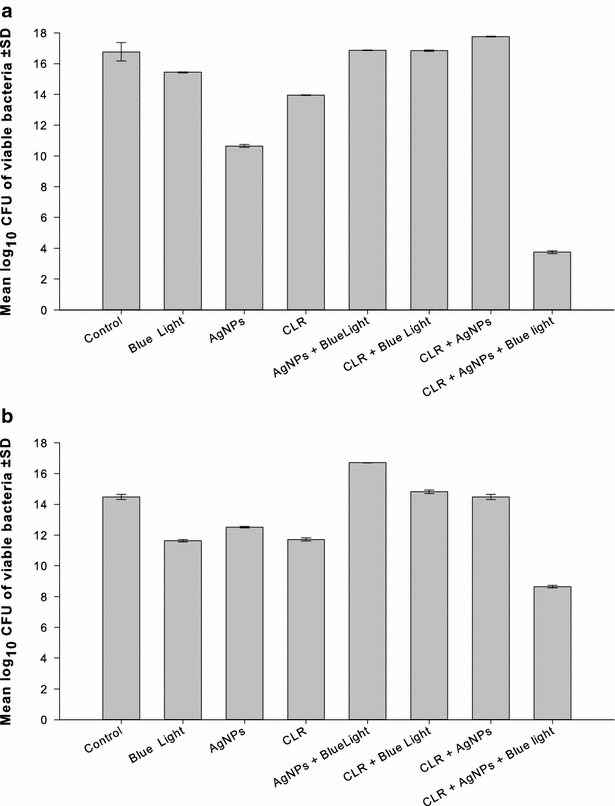
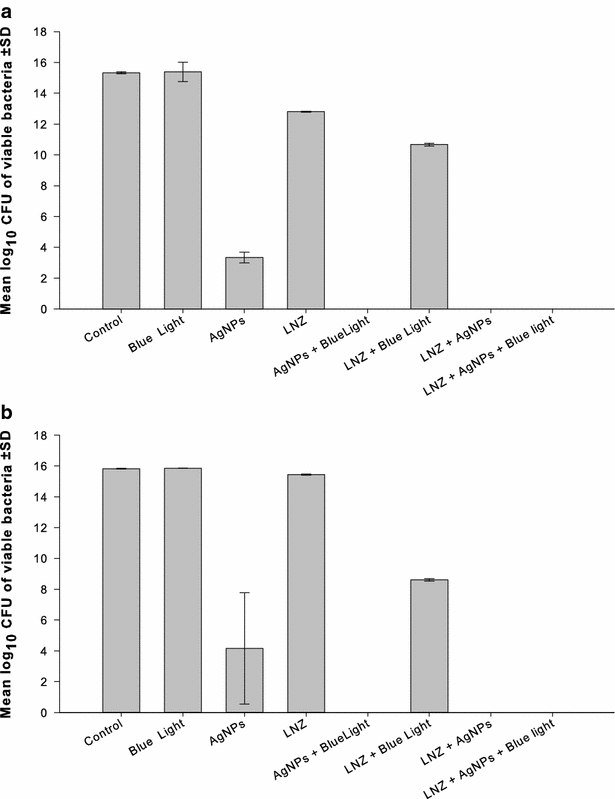
Results: The bactericidal activity of AgNPs, at sub-MIC, and blue light was significantly (p < 0.001) enhanced when both agents were applied in combination compared to each agent alone. Similarly, synergistic interactions were observed when AgNPs were combined with amoxicillin, azithromycin, clarithromycin or linezolid in 30-40 % of the double combinations with no observed antagonistic interaction against the tested isolates. Combination of the AgNPs with vancomycin did not result in enhanced killing against all isolates tested. The antimicrobial activity against MRSA isolates was significantly enhanced in triple combinations of AgNPs, blue light and antibiotic, compared to treatments involving one or two agents. The bactericidal activities were highest when azithromycin or clarithromycin was included in the triple therapy compared to the other antibiotics tested.
Conclusions: A new strategy can be used to combat serious infections caused by MRSA by combining AgNPs, blue light, and antibiotics. This triple therapy may include antibiotics, which have been proven to be ineffective against MRSA. The suggested approach would be useful to face the fast-growing drug-resistance with the slow development of new antimicrobial agents, and to preserve last resort antibiotics such as vancomycin.
Keywords: Azithromycin; Checkerboard assay; Clarithromycin; Double and triple combinations; Linezolid; Multidrug-resistance; Nonconventional antimicrobials; Vancomycin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro antibacterial effects of Tanreqing injection combined with vancomycin or linezolid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 May 30;18(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2231-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29848316 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Synergistic Effect of Vancomycin and Some Antibacterial Agents Against Clinical Methicillin-Resistant and Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus Isolates.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Mar;26(3):218-226. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2019.0003. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 31424323
-
A silver lining in MRSA treatment: The synergistic action of poloxamer-stabilized silver nanoparticles and methicillin against antimicrobial resistance.Microb Pathog. 2024 Dec;197:107087. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.107087. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39481693
-
Overcoming Methicillin-Resistance Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Using Antimicrobial Peptides-Silver Nanoparticles.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;11(7):951. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070951. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the synergistic sensitization of natural products and antibiotics: An effective strategy to combat MRSA.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Jan 5;281:117012. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117012. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39509947 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in MRSA treatment: the role of berberine in enhancing antibiotic therapy.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Dec 27;24(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03692-9. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39731013 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutics and delivery vehicles for local treatment of osteomyelitis.J Orthop Res. 2020 Oct;38(10):2091-2103. doi: 10.1002/jor.24689. Epub 2020 Apr 21. J Orthop Res. 2020. PMID: 32285973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of silver nano-drug using Juniperus excelsa and its synergistic antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria for wound dressing applications.3 Biotech. 2021 Jun;11(6):255. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02782-z. Epub 2021 May 8. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33987072 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical Approaches on Antimicrobial Resistance: Prospects and Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Aug 14;10(8):981. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10080981. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of Contact Lens Disinfection by Combining Disinfectant with Visible Light Irradiation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep 3;17(17):6422. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176422. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32899295 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

