MicroRNA-15b regulates reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) expression in human uterine leiomyoma
- PMID: 27530410
- PMCID: PMC4988044
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-016-0180-y
MicroRNA-15b regulates reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) expression in human uterine leiomyoma
Abstract
Background: Human uterine leiomyoma (fibroids; LYO) are the most common benign neoplasms in reproductive-aged women. Dysregulated extracellular matrix and irregular LYO reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) expression are thought to be mediated by aberrant microRNA (miR) expression. The relationship of miR-15b and RECK expression in LYO has not been studied.
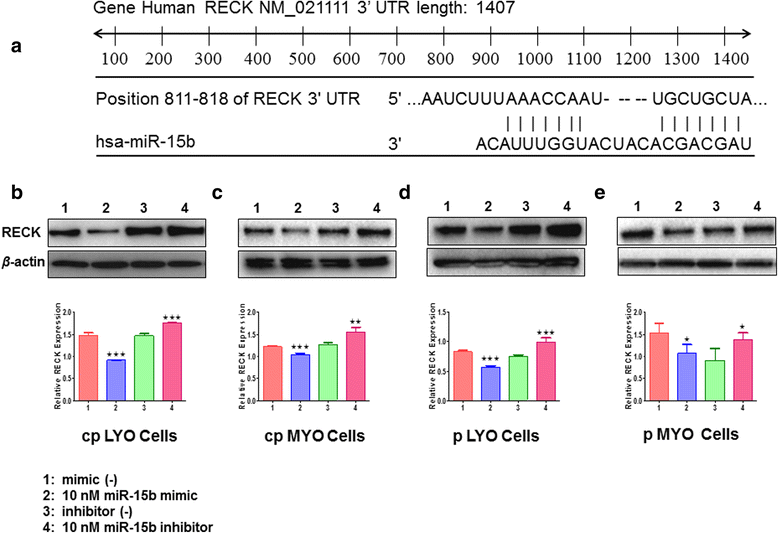
Methods: The expression levels of miR-15b and RECK were determined by quantitative RT-PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry in cultures derived from commercial primary leiomyoma (cpLYO) and myometrial (cpMYO) cell lines and leiomyoma (pLYO) and myometrium (pMYO) tissue from surgical samples respectively. The relationship between miR-15b and RECK expression in cpLYO and pLYO (compared to their respective myometrial controls) was evaluated following transfection of cell cultures with either miR-15b mimic or inhibitor.
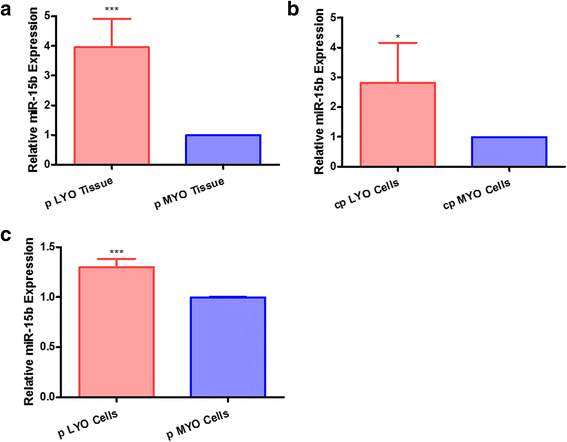
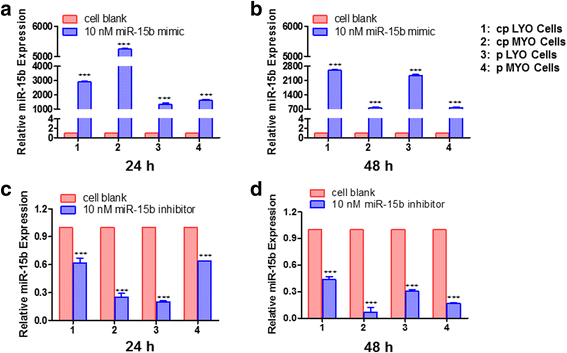
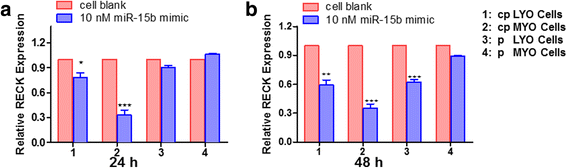
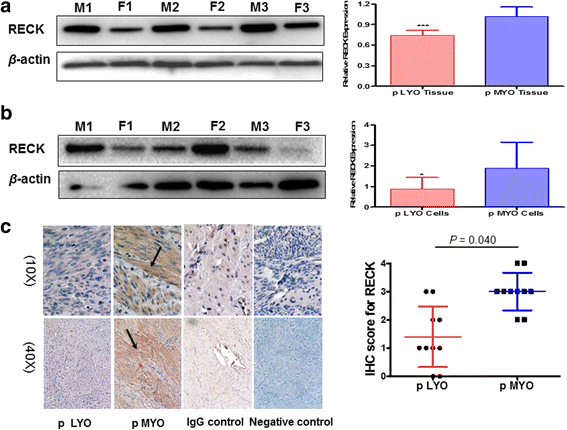
Results: Elevated levels of miR-15b were observed in cpLYO (2.82-fold; p = 0.04) and pLYO cell (1.30-fold; p = 0.0001) cultures respectively compared to corresponding MYO cell controls. Following transfection with miR-15b mimic, cpLYO cells (0.62-fold; p < 0.0001) and pLYO cells (0.68-fold; p < 0.0001) demonstrated reduced RECK protein expression. Following transfection with miR-15b inhibitor, cpLYO cells (1.20-fold; p < 0.0001) and pLYO cells (1.31-fold; p = 0.0007) demonstrated elevated RECK protein expression. RECK protein expression was reduced in pLYO tissues (0.73-fold; p < 0.0001) and pLYO (0.47-fold; p = 0.047) cells when compared to the corresponding MYO tissue controls.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that miR-15b negatively regulates RECK expression in LYO, and increased miR-15b and decreased RECK expression may contribute to the pathobiology of LYO. The functional significance of miR-15b and RECK expression warrants further investigation as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of human LYO.
Keywords: Fibroids; Myometrium; RECK; Uterine leiomyoma; miR-15b.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNA-200b and microRNA-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs.RNA Biol. 2015;12(3):276-89. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017208. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826661 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA 21a-5p overexpression impacts mediators of extracellular matrix formation in uterine leiomyoma.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018 May 11;16(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12958-018-0364-8. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29747655 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-374b-5p suppresses RECK expression and promotes gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Dec 14;20(46):17439-47. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17439. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25516656 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the development and pathobiology of uterine leiomyomata: does evidence support future strategies for clinical intervention?Hum Reprod Update. 2014 Sep-Oct;20(5):670-87. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmu017. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Hum Reprod Update. 2014. PMID: 24706045 Review.
-
RECKing MMP: relevance of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target for cancer (a review).Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Sep;12(7):718-25. doi: 10.2174/187152012802650237. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22292753 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of miRNA and Related Pathways in Pathophysiology of Uterine Fibroids-From Bench to Bedside.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 24;21(8):3016. doi: 10.3390/ijms21083016. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32344726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation in MicroRNA Expression Profile of Uterine Leiomyoma with Endometrial Cavity Distortion and Endometrial Cavity Non-Distortion.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 25;19(9):2524. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092524. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149651 Free PMC article.
-
miR-335-5p Inhibits Progression of Uterine Leiomyoma by Targeting ARGLU1.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 17;2022:2329576. doi: 10.1155/2022/2329576. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9760527. doi: 10.1155/2023/9760527. PMID: 35082911 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
RECK as a Potential Crucial Molecule for the Targeted Treatment of Sepsis.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 6;18:1787-1813. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S501856. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39931174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-15b-5p facilitates the tumorigenicity by targeting RECK and predicts tumour recurrence in prostate cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Mar;22(3):1855-1863. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13469. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29363862 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

