The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor teneligliptin functions as antioxidant on human endothelial cells exposed to chronic hyperglycemia and metabolic high-glucose memory
- PMID: 27530507
- PMCID: PMC5435779
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-016-1052-0
The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor teneligliptin functions as antioxidant on human endothelial cells exposed to chronic hyperglycemia and metabolic high-glucose memory
Abstract
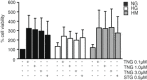
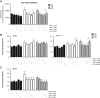
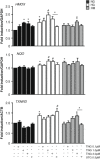
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors are widely used in type 2 diabetes. Endothelium plays a crucial role maintaining vascular integrity and function. Chronic exposure to high glucose drives to endothelial dysfunction generating oxidative stress. Teneligliptin is a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor with antioxidant properties. This study is aimed to verify a potential protective action of teneligliptin in endothelial cells exposed to high glucose. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were cultured under normal (5 mmol/L) or high glucose (25 mmol/L) during 21 days, or at high glucose during 14 days followed by 7 days at normal glucose, to reproduce the high-metabolic memory state. During this period, different concentrations of teneligliptin (0.1, 1.0 and 3.0 µmol/L) or sitagliptin (0.5 µmol/L) were added to cells. Ribonucleic acid and protein expression were assessed for antioxidant response, proliferation, apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress markers. Teneligliptin promotes the antioxidant response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, reducing ROS levels and inducing Nrf2-target genes messenger ribonucleic acid expression. Teneligliptin, but not sitagliptin, reduces the expression of the nicotine amide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase regulatory subunit P22 -phox , however, both blunt the high glucose-induced increase of TXNIP. Teneligliptin improves proliferation rates in human umbilical vein endothelial cells exposed to high glucose, regulating the expression of cell-cycle inhibitors markers (P53, P21 and P27), and reducing proapoptotic genes (BAX and CASP3), while promotes BCL2 expression. Teneligliptin ameliorates high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress reducing the expression of several markers (BIP, PERK, ATF4, CHOP, IRE1a and ATF6). Teneligliptin has antioxidant properties, ameliorates oxidative stress and apoptotic phenotype and it can overcome the metabolic memory effect, induced by chronic exposure to high glucose in human endothelial cells.
Keywords: Antioxidant; DPP-4 inhibitors; Diabetes; Endothelial dysfunction; High glucose; Metabolic memory; Teneligliptin and sitagliptin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Figures


Similar articles
-
Teneligliptin enhances the beneficial effects of GLP-1 in endothelial cells exposed to hyperglycemic conditions.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 1;9(10):8898-8910. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22849. eCollection 2018 Feb 6. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29507662 Free PMC article.
-
The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor teneligliptin improved endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance in the SHR/NDmcr-cp rat model of metabolic syndrome.Hypertens Res. 2014 Jul;37(7):629-35. doi: 10.1038/hr.2014.53. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Hypertens Res. 2014. PMID: 24621463
-
Teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, attenuated pro-inflammatory phenotype of perivascular adipose tissue and inhibited atherogenesis in normoglycemic apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice.Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;96-98:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Vascul Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28347868
-
Teneligliptin : expectations for its pleiotropic action.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015 Feb;16(3):417-26. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2015.1000301. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015. PMID: 25597385 Review.
-
[Pharmacological and clinical profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor teneligliptin hydrobromide hydrate (TENELIA(®)].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013 Sep;142(3):134-43. doi: 10.1254/fpj.142.134. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 24025495 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Unique Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Profile of Teneligliptin: Implications for Clinical Practice.Drugs. 2019 May;79(7):733-750. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01086-0. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30982160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Teneligliptin Co-Infusion Alleviates Morphine Tolerance by Inhibition of Spinal Microglial Cell Activation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jul 24;12(7):1478. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071478. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508016 Free PMC article.
-
Sitagliptin ameliorates oxidative stress in experimental diabetic nephropathy by diminishing the miR-200a/Keap-1/Nrf2 antioxidant pathway.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017 Jun 7;10:207-222. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S132537. eCollection 2017. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2017. PMID: 28652790 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Study Comparing Vildagliptin vs Glibenclamide on Glucose Variability and Endothelial Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Hypertension.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Sep 15;13:3221-3229. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S257096. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32982353 Free PMC article.
-
Linagliptin unmasks specific antioxidant pathways protective against albuminuria and kidney hypertrophy in a mouse model of diabetes.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 6;13(7):e0200249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200249. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29979777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Griendling KK, FitzGerald G. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular injury: Part I: basic mechanisms and in vivo monitoring of ROS. Circulation . 2003;108:1912–1916. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000093660.86242.BB. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

