The gut microbiota: a key regulator of metabolic diseases
- PMID: 27530685
- PMCID: PMC5227294
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.10.144
The gut microbiota: a key regulator of metabolic diseases
Abstract
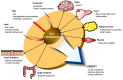
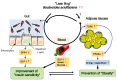
The prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes, two closely linked metabolic disorders, is increasing worldwide. Over the past decade, the connection between these disorders and the microbiota of the gut has become a major focus of biomedical research, with recent studies demonstrating the fundamental role of intestinal microbiota in the regulation and pathogenesis of metabolic disorders. Because of the complexity of the microbiota community, however, the underlying molecular mechanisms by which the gut microbiota is associated with metabolic disorders remain poorly understood. In this review, we summarize recent studies that investigate the role of the microbiota in both human subjects and animal models of disease and discuss relevant therapeutic targets for future research. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(10): 536-541].
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Gut microbiota and immune crosstalk in metabolic disease].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):1-18. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017008. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682223 Review. French.
-
Gut microbiota, obesity and metabolic disorders.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2017 Dec;63(4):337-344. doi: 10.23736/S1121-421X.17.02376-5. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2017. PMID: 28927249 Review.
-
Gut microbiota in health and disease: an overview focused on metabolic inflammation.Benef Microbes. 2016;7(2):181-94. doi: 10.3920/bm2015.0062. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Benef Microbes. 2016. PMID: 26645350 Review.
-
Connection between gut microbiome and the development of obesity.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;38(11):1987-1998. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03623-x. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31367997 Review.
-
The crosstalk between gut microbiota and obesity and related metabolic disorders.Future Microbiol. 2016 Jun;11:825-36. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2015-0024. Epub 2016 May 18. Future Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27192213 Review.
Cited by
-
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation and Other Gut Microbiota Manipulation Strategies.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 7;10(12):2424. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122424. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of the Intestinal Microbiota in Diagnosing the Progression of Diabetes and the Presence of Cardiovascular Complications.J Diabetes Res. 2018 Nov 12;2018:5205126. doi: 10.1155/2018/5205126. eCollection 2018. J Diabetes Res. 2018. PMID: 30539026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota-derived metabolites contribute negatively to hindgut barrier function development at the early weaning goat model.Anim Nutr. 2022 Apr 21;10:111-123. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.04.004. eCollection 2022 Sep. Anim Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35663372 Free PMC article.
-
A specific gut microbiota signature is associated with an enhanced GLP-1 and GLP-2 secretion and improved metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes after metabolic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 17;14:1181744. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1181744. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37916149 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Capsaicin in Metabolic Syndrome.Nutrients. 2018 May 17;10(5):630. doi: 10.3390/nu10050630. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29772784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

