Making sense of the relationships between Ne, Nb and Nc towards defining conservation thresholds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)
- PMID: 27530910
- PMCID: PMC5026759
- DOI: 10.1038/hdy.2016.62
Making sense of the relationships between Ne, Nb and Nc towards defining conservation thresholds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)
Abstract
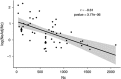
Effective population size over a generation (Ne) or over a reproductive cycle (Nb) and the adult census size (Nc) are important parameters in both conservation and evolutionary biology. Ne provides information regarding the rate of loss of genetic diversity and can be tracked back in time to infer demographic history of populations, whereas Nb may often be more easily quantified than Nc for short-term abundance monitoring. In this study, we propose (1) an empirical context to Waples et al. (2014) who introduced a correction to bias due to overlapping generations, and (2) a mathematical relationship between Ne and Nb for direct application in Atlantic salmon populations in Québec, Canada. To achieve this, we investigate the relationships between Ne, Nb and Nc in 10 Atlantic salmon populations, Canada, for which we genotyped 100 randomly sampled young-of-the year individuals for 5 consecutive years. The results show a positive correlation between Ne, Nb and Nc, suggesting that Nb is an indicative parameter for tracking effective population size and abundance of Atlantic salmon. However, our model allows predicting Nc from Nb values at 27% that can be partly explained by high variance in Nb/Nc both among populations (37%) and among years (19%). This result illustrates the need for thorough calibration of Nb/Nc before using Nb in monitoring programs, as well as a full understanding of the limits of such an approach. Finally, we discuss the importance of these results for the management of wild populations.
Figures


References
-
- Allendorf FW, Phelps SR. (1981). Use of allelic frequencies to describe population structure. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 38: 1507–1514.
-
- Araki H, Waples R, Ardren W, Cooper B, Blouin M. (2007). Effective population size of steelhead trout: influence of variance in reproductive success, hatchery programs, and genetic compensation between life-history forms. Mol Ecol 16: 953–966. - PubMed
-
- Ardren W, Kapuscinski A. (2003). Demographic and genetic estimates of effective population size (Ne) reveals genetic compensation in steelhead trout. Mol Ecol 12: 35–49. - PubMed
-
- Berry O, Kirkwood R. (2010). Measuring recruitment in an invasive species to determine eradication potential. J Wildl Management 74: 1661–1670.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

