Years of life gained by multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: 21 years follow-up on the Steno-2 randomised trial
- PMID: 27531506
- PMCID: PMC5506099
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-016-4065-6
Years of life gained by multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: 21 years follow-up on the Steno-2 randomised trial
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: The aim of this work was to study the potential long-term impact of a 7.8 years intensified, multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria in terms of gained years of life and years free from incident cardiovascular disease.
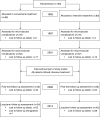
Methods: The original intervention (mean treatment duration 7.8 years) involved 160 patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria who were randomly assigned (using sealed envelopes) to receive either conventional therapy or intensified, multifactorial treatment including both behavioural and pharmacological approaches. After 7.8 years the study continued as an observational follow-up with all patients receiving treatment as for the original intensive-therapy group. The primary endpoint of this follow-up 21.2 years after intervention start was difference in median survival time between the original treatment groups with and without incident cardiovascular disease. Non-fatal endpoints and causes of death were adjudicated by an external endpoint committee blinded for treatment allocation.
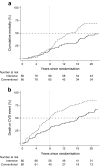
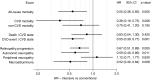
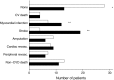
Results: Thirty-eight intensive-therapy patients vs 55 conventional-therapy patients died during follow-up (HR 0.55 [95% CI 0.36, 0.83], p = 0.005). The patients in the intensive-therapy group survived for a median of 7.9 years longer than the conventional-therapy group patients. Median time before first cardiovascular event after randomisation was 8.1 years longer in the intensive-therapy group (p = 0.001). The hazard for all microvascular complications was decreased in the intensive-therapy group in the range 0.52 to 0.67, except for peripheral neuropathy (HR 1.12).
Conclusions/interpretation: At 21.2 years of follow-up of 7.8 years of intensified, multifactorial, target-driven treatment of type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria, we demonstrate a median of 7.9 years of gain of life. The increase in lifespan is matched by time free from incident cardiovascular disease.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov registration no. NCT00320008.
Funding: The study was funded by an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk A/S.
Keywords: Albuminuria; Cardiovascular disease; Diabetes complications; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Diabetic nephropathy; Diabetic neuropathy; Diabetic retinopathy; Follow-up studies; Humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
The study was funded by an unrestricted grant from Novo Nordisk A/S. Novo Nordisk A/S were not in any way involved in study design or in data collection, analysis or interpretation, but have had the opportunity to read and comment on the manuscript before submission.
Duality of interest
BC is employed at Steno Diabetes Center, which is owned by Novo Nordisk A/S, and has equity share in Novo Nordisk A/S. PR has equity interest in Novo Nordisk A/S, research contracts with AbbVie, Novo Nordisk and Novartis and has received consulting honoraria from AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingellheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Astellas and AbbVie) (all to institution). HLA is a consultant at Steno Diabetes Center. HHP has equity interest in Merck and has received consulting honoraria from AbbVie and Novartis. OP has equity interest in Novo Nordisk A/S. The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research is an independent Research Center at the University of Copenhagen partially funded by an unrestricted donation from the Novo Nordisk Foundation (
Contribution statement
OP conceived and designed the original Steno-2 study, devised and supervised the 21.2 years follow-up, acquired all funding throughout the study and provided key content to the manuscript. HHP contributed to the conception and supervision of the original Steno-2 study and provided key content to the manuscript. PG acquired all data up to the 13.3 years examination, handled patient care during the intervention period, planned the 21.2 years follow-up and supervised data acquisition and processing in the present follow-up. JO coordinated and performed the 21.2 years follow-up, acquired all data for the 21.2 years follow-up, supervised laboratory work and patient evaluations, processed data and performed statistical work. BC planned, conducted and supervised statistical work, provided additional analyses and figures, contributed to data interpretation and compiled the ESM. PR supervised and facilitated all work performed at Steno Diabetes Center (i.e. the patient assessments for the long-term follow-up), was responsible for quality assurance/quality control of the performed measures, provided key intellectual content to the discussion section and critically reviewed the manuscript. HLA provided and interpreted data regarding retinopathy, provided key intellectual content and critically reviewed the manuscript. The manuscript was drafted by PG and JO with contributions from all other authors. All authors gave final approval for the paper to be published. OP, HHP and PG are guarantors of this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
Diabetes: Steno-2 - a small study with a big heart.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Dec;12(12):692-694. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.172. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27716752 No abstract available.
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB et al (2015) Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach. Update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia 58:429–442 - PubMed
-
- Murphy SA, Cannon CP, Wiviott SD, McCabe CH, Braunwald E. Reduction in recurrent cardiovascular events with intensive lipid-lowering statin therapy compared with moderate lipid-lowering statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes from the PROVE IT-TIMI 22 (Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy-Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction 22) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:2358–2362. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

