Direct Functional Interaction of the Kinesin-13 Family Member Kinesin-like Protein 2A (Kif2A) and Arf GAP with GTP-binding Protein-like, Ankyrin Repeats and PH Domains1 (AGAP1)
- PMID: 27531749
- PMCID: PMC5076806
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.732479
Direct Functional Interaction of the Kinesin-13 Family Member Kinesin-like Protein 2A (Kif2A) and Arf GAP with GTP-binding Protein-like, Ankyrin Repeats and PH Domains1 (AGAP1)
Erratum in
-
Direct functional interaction of the kinesin-13 family member kinesin-like protein 2A (Kif2A) and Arf GAP with GTP-binding protein-like, ankyrin repeats and PH domains 1 (AGAP1).J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 2;291(49):25761. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A116.732479. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27913662 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
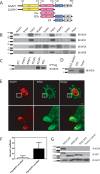
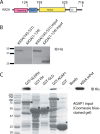
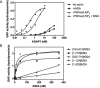
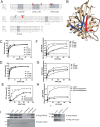
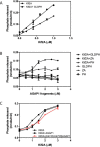
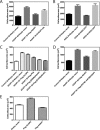
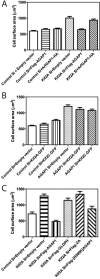
The molecular basis for control of the cytoskeleton by the Arf GTPase-activating protein AGAP1 has not been characterized. AGAP1 is composed of G-protein-like (GLD), pleckstrin homology (PH), Arf GAP, and ankyrin repeat domains. Kif2A was identified in screens for proteins that bind to AGAP1. The GLD and PH domains of AGAP1 bound the motor domain of Kif2A. Kif2A increased GAP activity of AGAP1, and a protein composed of the GLD and PH domains of AGAP1 increased ATPase activity of Kif2A. Knockdown (KD) of Kif2A or AGAP1 slowed cell migration and accelerated cell spreading. The effect of Kif2A KD on spreading could be rescued by expression of Kif2A-GFP or FLAG-AGAP1, but not by Kif2C-GFP. The effect of AGAP1 KD could be rescued by FLAG-AGAP1, but not by an AGAP1 mutant that did not bind Kif2A efficiently, ArfGAP1-HA or Kif2A-GFP. Taken together, the results support the hypothesis that the Kif2A·AGAP1 complex contributes to control of cytoskeleton remodeling involved in cell movement.
Keywords: ADP ribosylation factor (ARF); AGAP1; Arf GTPase-activating protein; GTPase activating protein (GAP); Kif2A; PH domain; cell biology; enzyme; kinesin; kinesin-13; protein complex; small GTPase.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arf GAPs and molecular motors.Small GTPases. 2019 May;10(3):196-209. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1308850. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28430047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGAP1, an endosome-associated, phosphoinositide-dependent ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein that affects actin cytoskeleton.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 13;277(50):48965-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202969200. Epub 2002 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12388557
-
Direct functional interaction of the kinesin-13 family member kinesin-like protein 2A (Kif2A) and Arf GAP with GTP-binding protein-like, ankyrin repeats and PH domains 1 (AGAP1).J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 2;291(49):25761. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A116.732479. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27913662 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
AGAP1 regulates subcellular localization of FilGAP and control cancer cell invasion.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Feb 12;522(3):676-683. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.147. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31785816
-
Arf GAPs as Regulators of the Actin Cytoskeleton-An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 21;20(2):442. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020442. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Arf GAPs and molecular motors.Small GTPases. 2019 May;10(3):196-209. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1308850. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28430047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Randazzo P. A., Inoue H., and Bharti S. (2007) Arf GAPs as regulators of the actin cytoskeleton. Biol. Cell 99, 583–600 - PubMed
-
- Randazzo P. A., and Kahn R. A. (1994) GTP Hydrolysis by ADP-ribosylation factor is dependent on both an ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-Activating protein and acid phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 10758–10763 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

