Abundant protein phosphorylation potentially regulates Arabidopsis anther development
- PMID: 27531888
- PMCID: PMC5014169
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erw293
Abundant protein phosphorylation potentially regulates Arabidopsis anther development
Abstract
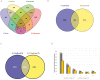
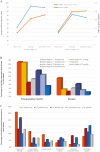
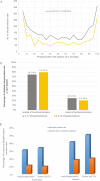
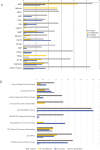
As the male reproductive organ of flowering plants, the stamen consists of the anther and filament. Previous studies on stamen development mainly focused on single gene functions by genetic methods or gene expression changes using comparative transcriptomic approaches, especially in model plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana However, studies on Arabidopsis anther protein expression and post-translational modifications are still lacking. Here we report proteomic and phosphoproteomic studies on developing Arabidopsis anthers at stages 4-7 and 8-12. We identified 3908 high-confidence phosphorylation sites corresponding to 1637 phosphoproteins. Among the 1637 phosphoproteins, 493 were newly identified, with 952 phosphorylation sites. Phosphopeptide enrichment prior to LC-MS analysis facilitated the identification of low-abundance proteins and regulatory proteins, thereby increasing the coverage of proteomic analysis, and facilitated the analysis of more regulatory proteins. Thirty-nine serine and six threonine phosphorylation motifs were uncovered from the anther phosphoproteome and further analysis supports that phosphorylation of casein kinase II, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and 14-3-3 proteins is a key regulatory mechanism in anther development. Phosphorylated residues were preferentially located in variable protein regions among family members, but they were they were conserved across angiosperms in general. Moreover, phosphorylation might reduce activity of reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes and hamper brassinosteroid signaling in early anther development. Most of the novel phosphoproteins showed tissue-specific expression in the anther according to previous microarray data. This study provides a community resource with information on the abundance and phosphorylation status of thousands of proteins in developing anthers, contributing to understanding post-translational regulatory mechanisms during anther development.
Keywords: Anther development; Arabidopsis; mass spectrometry; phosphoproteomics.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global Quantitative Proteomics Studies Revealed Tissue-Preferential Expression and Phosphorylation of Regulatory Proteins in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 25;21(17):6116. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176116. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32854314 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses reveal extensive phosphorylation of regulatory proteins in developing rice anthers.Plant J. 2015 Nov;84(3):527-44. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13019. Epub 2015 Oct 10. Plant J. 2015. PMID: 26360816
-
Regulation of Arabidopsis early anther development by the mitogen-activated protein kinases, MPK3 and MPK6, and the ERECTA and related receptor-like kinases.Mol Plant. 2008 Jul;1(4):645-58. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssn029. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Mol Plant. 2008. PMID: 19825569
-
Control of anther cell differentiation: a teamwork of receptor-like kinases.Sex Plant Reprod. 2009 Dec;22(4):221-8. doi: 10.1007/s00497-009-0106-3. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Sex Plant Reprod. 2009. PMID: 20033443 Review.
-
Phosphoproteomic Approaches for Identifying Phosphatase and Kinase Substrates.Molecules. 2023 Apr 24;28(9):3675. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093675. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175085 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Phosphorylation of the Cytosolic Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Isozyme G6PD6 in Phosphate-Resupplied Arabidopsis thaliana Suspension Cells and Seedlings.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;13(1):31. doi: 10.3390/plants13010031. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202338 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analyses provide evidence for extensive phosphorylation of regulatory proteins in the rhizobia-legume symbiosis.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;100(3):265-283. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00857-3. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30989446
-
Application of a Sensitive and Reproducible Label-Free Proteomic Approach to Explore the Proteome of Individual Meiotic-Phase Barley Anthers.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Apr 2;10:393. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00393. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31001307 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals the Response of Starch Metabolism to High-Temperature Stress in Rice Endosperm.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10546. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910546. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638888 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analyses Reveal a Complex Network Regulating Pollen Abortion and Potential Candidate Proteins in TCMS Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 8;23(12):6428. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126428. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baerenfaller K, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Svozil J, Hull R, Russenberger D, Bischof S, Lu Q, Gruissem W, Baginsky S. 2011. pep2pro: a new tool for comprehensive proteome data analysis to reveal information about organ-specific proteomes in Arabidopsis thaliana . Integrative Biology 3, 225–237. - PubMed
-
- Bogre L, Okresz L, Henriques R, Anthony RG. 2003. Growth signalling pathways in Arabidopsis and the AGC protein kinases. Trends in Plant Science 8, 424–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

