Cannabinoid Type 2 (CB2) Receptors Activation Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Associated Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 27531971
- PMCID: PMC4969295
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00321
Cannabinoid Type 2 (CB2) Receptors Activation Protects against Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Associated Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Rotenone Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
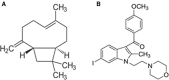
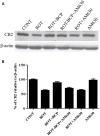
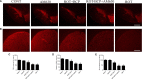
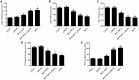
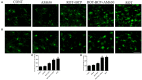
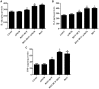
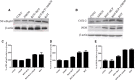
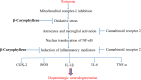
The cannabinoid type two receptors (CB2), an important component of the endocannabinoid system, have recently emerged as neuromodulators and therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson's disease (PD). The downregulation of CB2 receptors has been reported in the brains of PD patients. Therefore, both the activation and the upregulation of the CB2 receptors are believed to protect against the neurodegenerative changes in PD. In the present study, we investigated the CB2 receptor-mediated neuroprotective effect of β-caryophyllene (BCP), a naturally occurring CB2 receptor agonist, in, a clinically relevant, rotenone (ROT)-induced animal model of PD. ROT (2.5 mg/kg BW) was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) once daily for 4 weeks to induce PD in male Wistar rats. ROT injections induced a significant loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and DA striatal fibers, following activation of glial cells (astrocytes and microglia). ROT also caused oxidative injury evidenced by the loss of antioxidant enzymes and increased nitrite levels, and induction of proinflammatory cytokines: IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, as well as inflammatory mediators: NF-κB, COX-2, and iNOS. However, treatment with BCP attenuated induction of proinflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators in ROT-challenged rats. BCP supplementation also prevented depletion of glutathione concomitant to reduced lipid peroxidation and augmentation of antioxidant enzymes: SOD and catalase. The results were further supported by tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemistry, which illustrated the rescue of the DA neurons and fibers subsequent to reduced activation of glial cells. Interestingly, BCP supplementation demonstrated the potent therapeutic effects against ROT-induced neurodegeneration, which was evidenced by BCP-mediated CB2 receptor activation and the fact that, prior administration of the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 diminished the beneficial effects of BCP. The present study suggests that BCP has the potential therapeutic efficacy to elicit significant neuroprotection by its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities mediated by activation of the CB2 receptors.
Keywords: AM630; Parkinson's disease; Trans-caryophyllene; cannabinoid agonist; neurodegeneration; neuroprotection; rotenone; β-caryophyllene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effect of nerolidol against neuroinflammation and oxidative stress induced by rotenone.BMC Neurosci. 2016 Aug 22;17(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0293-4. BMC Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27549180 Free PMC article.
-
β-Caryophyllene, a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene attenuates doxorubicin-induced chronic cardiotoxicity via activation of myocardial cannabinoid type-2 (CB2) receptors in rats.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 May 1;304:158-167. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.02.028. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30836069
-
β-Caryophyllene, a phytocannabinoid attenuates oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, glial activation, and salvages dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of Parkinson disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Jul;418(1-2):59-70. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2733-y. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27316720
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
-
Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease and its potential as therapeutic target.Transl Neurodegener. 2015 Oct 12;4:19. doi: 10.1186/s40035-015-0042-0. eCollection 2015. Transl Neurodegener. 2015. PMID: 26464797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on the cannabinoid type-2 receptor and Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;15:1298166. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1298166. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38264546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of c-Abl Kinase in Microglial Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Impairment in Autolysosomal System.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;12(4):624-660. doi: 10.1007/s11481-017-9746-5. Epub 2017 May 2. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28466394 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cannabinoids in Therapy of Neurodegenerative Disorders and Inflammatory Diseases of the CNS.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 8;26(14):6570. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146570. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contribution of Microglia to Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4676. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094676. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33925154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of cannabinoid receptor 2 Q63R gene polymorphism in Lebanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;37(11):2933-2938. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4217-9. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 30032418
References
-
- Al Mansouri S., Ojha S., Al Maamari E., Al Ameri M., Nurulain S. M., Bahi A. (2014). The cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, β-caryophyllene, reduced voluntary alcohol intake and attenuated ethanol-induced place preference and sensitivity in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 124, 260–268. 10.1016/j.pbb.2014.06.025 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arumugam T. V., Cheng Y. L., Choi Y., Choi Y. H., Yang S., Yun Y. K., et al. . (2011). Evidence that γ-secretase-mediated notch signaling induces neuronal cell death via the nuclear factor-κB-Bcl-2- interacting mediator of cell death pathway in ischemic stroke. Mol. Pharmacol. 80, 23–31. 10.1124/mol.111.071076 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

