Burst Firing in the Electrosensory System of Gymnotiform Weakly Electric Fish: Mechanisms and Functional Roles
- PMID: 27531978
- PMCID: PMC4969294
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2016.00081
Burst Firing in the Electrosensory System of Gymnotiform Weakly Electric Fish: Mechanisms and Functional Roles
Abstract
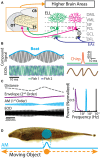
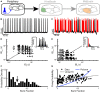
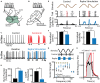
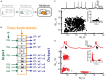
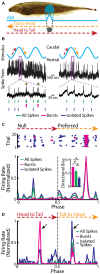
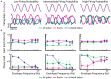
Neurons across sensory systems and organisms often display complex patterns of action potentials in response to sensory input. One example of such a pattern is the tendency of neurons to fire packets of action potentials (i.e., a burst) followed by quiescence. While it is well known that multiple mechanisms can generate bursts of action potentials at both the single-neuron and the network level, the functional role of burst firing in sensory processing is not so well understood to date. Here we provide a comprehensive review of the known mechanisms and functions of burst firing in processing of electrosensory stimuli in gymnotiform weakly electric fish. We also present new evidence from existing data showing that bursts and isolated spikes provide distinct information about stimulus variance. It is likely that these functional roles will be generally applicable to other systems and species.
Keywords: burst firing; directional selectivity; envelope; feature detection; neural coding; weakly electric fish.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural heterogeneities and stimulus properties affect burst coding in vivo.Neuroscience. 2010 Jun 16;168(1):300-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.03.012. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20298764 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin modulates optimized coding of natural stimuli through increased neural and behavioural responses via enhanced burst firing.J Physiol. 2020 Apr;598(8):1573-1589. doi: 10.1113/JP278940. Epub 2020 Mar 3. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32011728
-
Bursts and isolated spikes code for opposite movement directions in midbrain electrosensory neurons.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040339. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768279 Free PMC article.
-
Perception and coding of envelopes in weakly electric fishes.J Exp Biol. 2013 Jul 1;216(Pt 13):2393-402. doi: 10.1242/jeb.082321. J Exp Biol. 2013. PMID: 23761464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ionic and neuromodulatory regulation of burst discharge controls frequency tuning.J Physiol Paris. 2008 Jul-Nov;102(4-6):195-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2008.10.019. Epub 2008 Oct 18. J Physiol Paris. 2008. PMID: 18992813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Motion parallax in electric sensing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 16;115(3):573-577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1712380115. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29295924 Free PMC article.
-
Descending pathways generate perception of and neural responses to weak sensory input.PLoS Biol. 2018 Jun 25;16(6):e2005239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005239. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29939982 Free PMC article.
-
Is Neuromorphic MNIST Neuromorphic? Analyzing the Discriminative Power of Neuromorphic Datasets in the Time Domain.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 25;15:608567. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.608567. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33841072 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive neuromagnetic single-trial analysis of human neocortical population spikes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 16;118(11):e2017401118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017401118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33707209 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of burst spikes on linear and nonlinear signal transmission in spiking neurons.J Comput Neurosci. 2025 Mar;53(1):37-60. doi: 10.1007/s10827-024-00883-1. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Comput Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39560916 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

