Diagnosis and Anti-Reflux Therapy for GERD with Respiratory Symptoms: A Study Using Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-pH Monitoring
- PMID: 27532103
- PMCID: PMC4988652
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160139
Diagnosis and Anti-Reflux Therapy for GERD with Respiratory Symptoms: A Study Using Multichannel Intraluminal Impedance-pH Monitoring
Abstract
Background/aims: Respiratory symptoms are often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Although the role of multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH (MII-pH) monitoring in GERD is clear, little is known regarding the characteristics of patients with respiratory symptoms based on MII-pH monitoring and anti-reflux therapy. We evaluated a cohort of GERD patients to identify the MII-pH parameters of GERD-related respiratory symptoms and to assess the anti-reflux therapy outcomes.
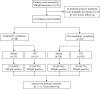
Methods: We undertook a prospective study of patients who were referred for GERD evaluation from January 2011 to January 2012. One hundred ninety-five patients underwent MII-pH monitoring and esophageal manometry, and one hundred sixty-five patients underwent invasive anti-reflux therapy that included laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication (LTF) and the Stretta procedure. The patient characteristics and MII-pH parameters were analyzed, and the symptom scores were assessed at baseline and at 1- and 3-year follow-up evaluations.
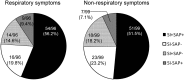
Results: Of the 195 patients, 96 (49.2%) exhibited respiratory symptoms and significantly more reflux episodes (70.7±29.3) than patients without respiratory symptoms (64.7±24.4, p = 0.044) based on the MII-pH monitoring results. Moreover, the group of patients with respiratory symptoms exhibited more proximal reflux episodes (35.2±21.3) than the non-respiratory symptomatic group (28.3±17.9, p = 0.013). One hundred twenty-five patients following the Stretta procedure (n = 60, 31 with respiratory symptoms) or LTF (n = 65, 35 with respiratory symptoms) completed the designated 3-year follow-up period and were included in the final analysis. The symptom scores after anti-reflux therapy all decreased relative to the corresponding baseline values (p<0.05), and there were no significant differences in the control of respiration between the Stretta procedure and LTF (p>0.05). However, LTF significantly reduced the recurrence (re-operation) rate compared with the Stretta procedure (0 vs. 19.4%, p = 0.006).
Conclusions: MII-pH monitoring effectively detected respiratory-related predictive parameters, including total/proximal reflux episodes and symptom correlations. We found that GERD patients with respiratory symptoms exhibited more proximal and total reflux episodes but not more acid-related episodes, as determined by MII-pH monitoring. Thus, such monitoring could be useful for diagnosing atypical GERD patients with respiratory symptoms. Furthermore, LTF exhibited a more significant effect on controlling typical symptoms in all GERD patients and reducing the recurrence rate than the Stretta procedure in patients with respiratory symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Stretta procedure and toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease-related extra-esophageal symptoms.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 7;21(45):12882-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12882. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26668513 Free PMC article.
-
Pre and post-operative evaluation of gastroesophageal reflux and esophageal motility in neurologically impaired children using combined pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance measurements.Pediatr Surg Int. 2013 Jun;29(6):545-51. doi: 10.1007/s00383-013-3295-7. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Pediatr Surg Int. 2013. PMID: 23519548 Free PMC article.
-
Combined esophageal multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring (MII -pH) in the diagnostics and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease and its complications.Pol Przegl Chir. 2011 Sep;83(9):488-96. doi: 10.2478/v10035-011-0076-7. Pol Przegl Chir. 2011. PMID: 22166737 Clinical Trial.
-
Indications of 24-h esophageal pH monitoring, capsule pH monitoring, combined pH monitoring with multichannel impedance, esophageal manometry, radiology and scintigraphy in gastroesophageal reflux disease?Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec;28(Suppl 1):S16-S21. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.06. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29199161 Review.
-
Utilising multichannel intraluminal impedance for diagnosing GERD: a review.Dis Esophagus. 2007;20(2):83-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00654.x. Dis Esophagus. 2007. PMID: 17439589 Review.
Cited by
-
Mind the Gap: Current Treatment Alternatives for GERD Patients Failing Medical Treatment and Not Ready for a Fundoplication.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2020 Dec 16;31(2):264-276. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000888. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2020. PMID: 33347088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Revisited.Clin Endosc. 2016 Sep;49(5):408-416. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.133. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Clin Endosc. 2016. PMID: 27744659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.Open Med (Wars). 2023 Oct 11;18(1):20230791. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0791. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37840752 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of reflux episodes in gastroesophageal reflux-induced chronic cough: a novel predictive indicator.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Aug 17;13:20406223221117455. doi: 10.1177/20406223221117455. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 36003286 Free PMC article.
-
Nissen fundoplication vs proton pump inhibitors for laryngopharyngeal reflux based on pH-monitoring and symptom-scale.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 21;23(19):3546-3555. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i19.3546. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28596691 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

