Vitamin Variation in Capsicum Spp. Provides Opportunities to Improve Nutritional Value of Human Diets
- PMID: 27532495
- PMCID: PMC4988645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161464
Vitamin Variation in Capsicum Spp. Provides Opportunities to Improve Nutritional Value of Human Diets
Abstract
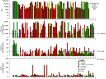
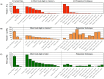
Chile peppers, native to the Americas, have spread around the world and have been integrated into the diets of many cultures. Much like their heat content, nutritional content can vary dramatically between different pepper types. In this study, a diverse set of chile pepper types were examined for nutrient content. Some pepper types were found to have high levels of vitamin A, vitamin C, or folate. Correlations between nutrient content, species, cultivation status, or geographic region were limited. Varietal selection or plant breeding offer tools to augment nutrient content in peppers. Integration of nutrient rich pepper types into diets that already include peppers could help combat nutrient deficiencies by providing a significant portion of recommended daily nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolomic study of marketable and unmarketable chili peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) classified by the fruit size and shape.Food Chem. 2025 Jul 15;480:143897. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143897. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40138826
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
-
The effects of ripening stage and processing systems on vitamin C content in sweet peppers (Capsicum annuum L.).Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2005 Feb;56(1):45-51. doi: 10.1080/09637480500081936. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2005. PMID: 16019314
-
Capsaicin accumulation in Capsicum spp. suspension cultures.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;318:327-34. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-959-1:327. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16673927
-
Capsicum annuum (hot pepper): An ancient Latin-American crop with outstanding bioactive compounds and nutraceutical potential. A review.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020 Nov;19(6):2972-2993. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12634. Epub 2020 Sep 27. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020. PMID: 33337034 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Dietary Supplementation with Capsicum Annum L on Performance, Hematology, Blood Biochemistry and Hepatic Antioxidant Status of Growing Rabbits.Animals (Basel). 2020 Nov 5;10(11):2045. doi: 10.3390/ani10112045. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33167395 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of the Varietal Type, Ripening Stage, and Growing Conditions on the Content and Profile of Sugars and Capsaicinoids in Capsicum Peppers.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;12(2):231. doi: 10.3390/plants12020231. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678946 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Na+/H+ Exchanger Gene Family in Capsicum annuum L.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 2;12:680457. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.680457. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34539731 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide genotyping of a novel Mexican Chile Pepper collection illuminates the history of landrace differentiation after Capsicum annuum L. domestication.Evol Appl. 2018 Jul 11;12(1):78-92. doi: 10.1111/eva.12651. eCollection 2019 Jan. Evol Appl. 2018. PMID: 30622637 Free PMC article.
-
Piquin chili, a wild spice: natural variation in nutraceutical contents.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 15;11:1360299. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1360299. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38685953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sherman PW, Billing J. Darwinian Gastronomy: Why We Use Spices Spices taste good because they are good for us. BioScience. 1999;49: 453–463.
-
- Pickersgill B. Relationships Between Weedy and Cultivated Forms in Some Species of Chili Peppers (Genus capsicum). Evolution. 1971;25: 683–691. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

