Transcriptome Profile of Near-Isogenic Soybean Lines for β-Conglycinin α-Subunit Deficiency during Seed Maturation
- PMID: 27532666
- PMCID: PMC4988716
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159723
Transcriptome Profile of Near-Isogenic Soybean Lines for β-Conglycinin α-Subunit Deficiency during Seed Maturation
Abstract
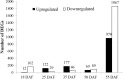
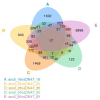
Crossing, backcrossing, and molecular marker-assisted background selection produced a soybean (Glycine max) near-isogenic line (cgy-2-NIL) containing the cgy-2 allele, which is responsible for the absence of the allergenic α-subunit of β-conglycinin. To identify α-null-related transcriptional changes, the gene expressions of cgy-2-NIL and its recurrent parent DN47 were compared using Illumina high-throughput RNA-sequencing of samples at 25, 35, 50, and 55 days after flowering (DAF). Seeds at 18 DAF served as the control. Comparison of the transcript profiles identified 3,543 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two genotypes, with 2,193 genes downregulated and 1,350 genes upregulated. The largest numbers of DEGs were identified at 55 DAF. The DEGs identified at 25 DAF represented a unique pattern of GO category distributions. KEGG pathway analyses identified 541 altered metabolic pathways in cgy-2-NIL. At 18DAF, 12 DEGs were involved in arginine and proline metabolism. The cgy-2 allele in the homozygous form modified the expression of several Cupin allergen genes. The cgy-2 allele is an alteration of a functional allele that is closely related to soybean protein amino acid quality, and is useful for hypoallergenic soybean breeding programs that aim to improve seed protein quality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The β-conglycinin deficiency in wild soybean is associated with the tail-to-tail inverted repeat of the α-subunit genes.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Feb;78(3):301-9. doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9865-y. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22193750
-
Profiles of embryonic nuclear protein binding to the proximal promoter region of the soybean β-conglycinin α subunit gene.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2015 Jan;17(1):147-52. doi: 10.1111/plb.12218. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2015. PMID: 24943483
-
Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping for Glycinin and β-Conglycinin Contents in Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.).J Agric Food Chem. 2016 May 4;64(17):3473-83. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00167. Epub 2016 Apr 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27070305
-
Improved protein quality in transgenic soybean expressing a de novo synthetic protein, MB-16.Transgenic Res. 2014 Jun;23(3):455-67. doi: 10.1007/s11248-013-9777-5. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Transgenic Res. 2014. PMID: 24435987
-
Using RNA-Seq to profile soybean seed development from fertilization to maturity.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059270. Epub 2013 Mar 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555009 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci for Soybean Seedling Shoot and Root Architecture Traits in an Inter-Specific Genetic Population.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 19;11:1284. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01284. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32973843 Free PMC article.
-
Soybean genetic resources contributing to sustainable protein production.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Nov;135(11):4095-4121. doi: 10.1007/s00122-022-04222-9. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 36239765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of sucrose synthase family in soybean and their expression in response to abiotic stress and seed development.PLoS One. 2022 Feb 25;17(2):e0264269. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264269. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2022 Sep 14;17(9):e0274409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274409. PMID: 35213642 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Soybean Mutants Lacking Abundant Seed Storage Proteins Are Impaired in Mobilization of Storage Reserves and Germination.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 31;5(14):8065-8075. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00128. eCollection 2020 Apr 14. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32309716 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of the effects of friction and exogenous gibberellin on germination in Abrus cantoniensis.Plant Signal Behav. 2022 Dec 31;17(1):2149113. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2022.2149113. Plant Signal Behav. 2022. PMID: 36448597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogawa T, Tayama E, Kitamura K, Kaizuma N. Genetic improvement of seed storage proteins using three variant alleles of 7S globulin subunits in soybean (Glycine max L.). Jpn J Breed. 1989;39: 137–147.
-
- Takahashi M, Uematsu Y, Kashiwaba K, Yagasaki K, Hajika M, Matsunaga R, et al. Accumulations of high levels of free amino acids in soybean seeds through integration of mutations conferring seed protein deficiency. Planta. 2003;217: 577–586. - PubMed
-
- Harada K, Hayashi M, Tsubokura Y. Genetic variation of globulin composition in Soybean Seeds. Agricultural Research Updates. 2013; 101–116.
-
- Ogawa A, Samoto M, Takahashi K. Soybean allergens and hypoallergenic soybean products. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. 2000;46: 271–279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

