Silibinin inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-mediated signaling, angiogenesis and lipogenesis in prostate cancer cells: In vitro evidence and in vivo functional imaging and metabolomics
- PMID: 27533043
- PMCID: PMC5637733
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.22537
Silibinin inhibits hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-mediated signaling, angiogenesis and lipogenesis in prostate cancer cells: In vitro evidence and in vivo functional imaging and metabolomics
Abstract
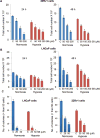
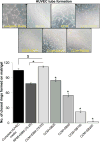
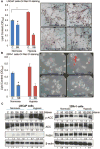
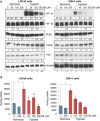
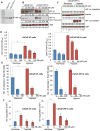
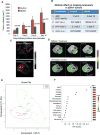
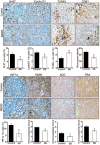
Hypoxia is associated with aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis in prostate cancer (PCa) patients suggesting that PCa growth and progression could be controlled via targeting hypoxia-induced signaling and biological effects. Here, we analyzed silibinin (a natural flavonoid) efficacy to target cell growth, angiogenesis, and metabolic changes in human PCa, LNCaP, and 22Rv1 cells under hypoxic condition. Silibinin treatment inhibited the proliferation, clonogenicity, and endothelial cells tube formation by hypoxic (1% O2 ) PCa cells. Interestingly, hypoxia promoted a lipogenic phenotype in PCa cells via activating acetyl-Co A carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FASN) that was inhibited by silibinin treatment. Importantly, silibinin treatment strongly decreased hypoxia-induced HIF-1α expression in PCa cells together with a strong reduction in hypoxia-induced NADPH oxidase (NOX) activity. HIF-1α overexpression in LNCaP cells significantly increased the lipid accumulation and NOX activity; however, silibinin treatment reduced HIF-1α expression, lipid levels, clonogenicity, and NOX activity even in HIF-1α overexpressing LNCaP cells. In vivo, silibinin feeding (200 mg/kg body weight) to male nude mice with 22Rv1 tumors, specifically inhibited tumor vascularity (measured by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI) resulting in tumor growth inhibition without directly inducing necrosis (as revealed by diffusion-weighted MRI). Silibinin feeding did not significantly affect tumor glucose uptake measured by FDG-PET; however, reduced the lipid synthesis measured by quantitative 1 H-NMR metabolomics. IHC analyses of tumor tissues confirmed that silibinin feeding decreased proliferation and angiogenesis as well as reduced HIF-1α, FASN, and ACC levels. Together, these findings further support silibinin usefulness against PCa through inhibiting hypoxia-induced signaling. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: hypoxia; hypoxia-inducible factor; lipogenesis; prostate cancer; silibinin.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, P276-00, inhibits HIF-1α and induces G2/M arrest under hypoxia in prostate cancer cells.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2012 Mar;15(1):15-27. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2011.51. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2012. PMID: 22083267
-
Magnolol suppresses hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via inhibition of HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway in human bladder cancer cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 May 1;85(9):1278-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.02.009. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23416116
-
Silibinin inhibits expression of HIF-1alpha through suppression of protein translation in prostate cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Dec 4;390(1):71-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.09.068. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19778521
-
Prostate cancer prevention by silibinin.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004 Feb;4(1):1-11. doi: 10.2174/1568009043481605. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 14965263 Review.
-
Natural products as potent inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in cancer therapy.Chin J Nat Med. 2020 Sep;18(9):696-703. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)60008-5. Chin J Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32928513 Review.
Cited by
-
Silibinin inhibits epithelial‑mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma through autophagy‑dependent Wnt/β‑catenin signaling.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1341-1350. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4521. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323735 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate cancer: Therapeutic prospect with herbal medicine.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021 Jul 8;2:100034. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2021.100034. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34909665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silibinin down-regulates PD-L1 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by interfering with tumor cell glycolytic metabolism.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Sep 15;690:108479. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108479. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32679194 Free PMC article.
-
iDMET: network-based approach for integrating differential analysis of cancer metabolomics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Nov 28;23(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05068-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36443658 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products remodel cancer-associated fibroblasts in desmoplastic tumors.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Nov;10(11):2140-2155. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 33304782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

