Epidemiological and Virological Characterization of Influenza B Virus Infections
- PMID: 27533045
- PMCID: PMC4988634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161195
Epidemiological and Virological Characterization of Influenza B Virus Infections
Abstract
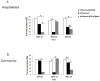
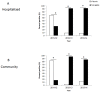
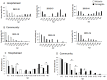
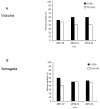
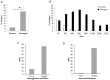
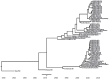
While influenza A viruses comprise a heterogeneous group of clinically relevant influenza viruses, influenza B viruses form a more homogeneous cluster, divided mainly into two lineages: Victoria and Yamagata. This divergence has complicated seasonal influenza vaccine design, which traditionally contained two seasonal influenza A virus strains and one influenza B virus strain. We examined the distribution of the two influenza B virus lineages in Israel, between 2011-2014, in hospitalized and in non-hospitalized (community) influenza B virus-infected patients. We showed that influenza B virus infections can lead to hospitalization and demonstrated that during some winter seasons, both influenza B virus lineages circulated simultaneously in Israel. We further show that the influenza B virus Yamagata lineage was dominant, circulating in the county in the last few years of the study period, consistent with the anti-Yamagata influenza B virus antibodies detected in the serum samples of affected individuals residing in Israel in the year 2014. Interestingly, we found that elderly people were particularly vulnerable to Yamagata lineage influenza B virus infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Wright PNG, Kawaoka Y (2006) Orthomyxoviruses In Fields Virology 5th edition: 1691–1740.
-
- Osterhaus AD, Rimmelzwaan GF, Martina BE, Bestebroer TM, Fouchier RA (2000) Influenza B virus in seals. Science 288: 1051–1053. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

